Back pain has become one of the most common ailments treated by doctors. It most often responds to nonsurgical treatments like heat, medicine, home exercises, and physical therapy. The intensity of back pain usually fades away within three months. However, in some cases, if the conservative treatments have failed to cure and the pain is persistent, our medical specialist can help you determine whether surgery is the best option. Sometimes, it is a realistic or essential choice for treating major musculoskeletal problems or nerve compression. Back surgery often improves accompanying pain or numbness that travels down to one or both legs or arms.
When do you need back surgery?
Back surgery (Spine surgery) may be needed for several reasons
- Degenerative spine disease – These are the most common conditions that need back surgery. Degenerative (wear and tear) diseases of the spine are commonly seen in older age group patients. Some common examples are – Lumbar canal stenosis (Decreased area for the nerves in the spine); Spondylolisthesis (Slippage of one bone over the other) and Disc prolapse (slipped disc/ Ruptured disc/Herniated disc).
- Spinal trauma – In cases of a major injury to the spine (Fractures/ Bone displacement etc..) due to accident or fall, the spine needs to be stabilized by surgery
- Spinal infections – Some types if infections (Bacterial/ Tuberculosis (TB) etc.) can affect the spine. In cases where the bone is destroyed or the nerve is compressed due to infection, surgery will be required to decompress the nerve and fix the spinal bones
- Spinal deformity – These are conditions where the spine bones are not in a normal alignment resulting in deformity of the back and compression of the nerves.
- Spinal tumors – Tumors affecting the spine (Primarily or spread form other areas) can cause back pain, bone destruction and nerve compression which will require surgery.
Any of the above diseases can cause compression of the nerves resulting in severe back pain, numbness or weakness of the limbs and difficulty in walking, during which surgery will be helpful.
What are the types of spine surgery?
There are numerous types of spine surgery. Each of them is decided based on the extent and severity of disease, condition of the patient and findings on the MRI of the patient
Some commonly performed surgeries are
- Discectomy – This is a procedure where the herniated or prolapsed disc is removed to free the nerves.
- Spinal canal decompression – Here, the space for the nerves inside the spinal canal is increased by removing a part of bone and ligament
- Spinal fusion and fixation – In this, screws and rod along with bone graft is used to fuse the adjacent bones, usually in cases of spinal trauma or instability
- Vertebroplasty/ Kyphoplasty – This is a procedure where cement is injected in to a weak (osteoporotic) and fractured bone to restore its strength and reduce pain
- Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: They are two different procedures and techniques which are used to treat osteoporosis-related compression fractures of the vertebrae. Both procedures include injecting glue-like bone components into the bone, which hardens and strengthens the bone.
- Nucleoplasty or Plasma disc decompression: Radiofrequency energy is used in this laser surgery to alleviate low back discomfort caused by a moderately herniated disc. A needle is inserted into the disc, and after inserting a plasma laser device into the needle and heating the tip, a field is created that vaporises the tissue in the disc. It relieves pressure & reduces sizes of nerves.
- Laminectomy and decompression of the spine: This procedure is mostly used when spinal stenosis causes a narrowing of the spinal canal. It results in numbness, discomfort, or weakness. The surgeon creates an opening in the spinal column by removing the bony walls of the vertebrae as well as any bone spurs to relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Spine Fusion: The surgeon removes the spinal disc between two or more vertebrae and then uses metal devices or bone grafts connected by screws to fuse the adjacent vertebrae. Spinal fusion can cause a loss of spine flexibility and requires a lengthy recovery period to allow the bone grafts to develop and fuse the vertebrae.
- Artificial Disc replacement: For patients with badly damaged discs, artificial disc replacement is considered an alternative to spinal fusion. The disc is removed and replaced with a synthetic disc that helps restore movement and height between the vertebrae.
- Discectomy: This type of surgery is performed to remove the herniated disc and is pressing on a nerve root or the spinal cord. The surgeon often combines laminectomy and Discectomy procedures.
- Foraminotomy: During this procedure, the surgeon enlarges the bone hole where a nerve root exits the spinal canal to avoid age-related joint thickening or bulging discs from resting on the nerve.
What are the benefits?
Doing spine surgery at the right time can prevent damage to the nerves coming to your arms and legs and in many cases give significant relief from the pain so that you can return to your daily normal activities and work. Many older individuals who avoid social gatherings and long-distance travel in apprehension of aggravating their back problem can actually go back to an active social life following a spine surgery.
The results of back surgery will be more than just a reduction in pain. It significantly reduces damage to blood vessels, nerves, and muscles, surgical complications, blood loss, and scarring. Certain other benefits include:
- You are more productive at work
- Free to return to work
- You will not require pain relief medication
- You will have a better mind
- You will be physically fit for everyday challenges
- You will be able to move around easily.
What are the risks involved?
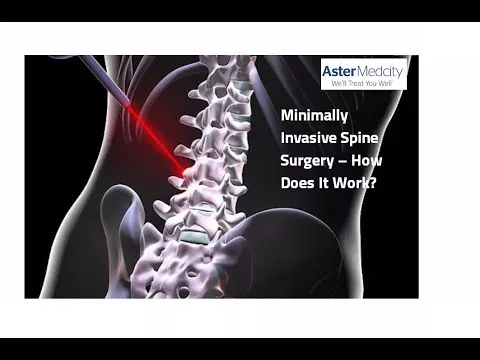
All surgeries carry a certain amount of risk and no surgery, however small can be completely devoid of risk. However, with advances in techniques, latest technology and modern peri-operative management protocols, the risk is considerably less these days than what it used to be. Minimally invasive spine surgery techniques reduce risk to back muscles, helping a patient to recover faster from the surgery with less post-operative pain as compared to conventional / open spine surgery.
Latest technological advances like intra-op 3D imaging, navigation and intra-operative monitoring can reduce the risk of damage to the nerves and increase the accuracy of spine surgeries.
Despite the above advances, a small percentage of patients can still have side-effects or complications as a result of spine surgery.
- Persistent post-op pain, either in the back or leg
- Infection
- Delayed wound healing
- Nerve injury – fresh post-operative weakness or numbness
- Implant related complications – Screw breakage, pullout
- Other systems – Heart attack, blood clots in the legs, Allergic reaction to drugs/ anesthesia
The majority of patients who have undergone back surgery experience very few issues.
However, any operation carries some level of risk, which includes:
- Heart attack
- Disk herniation
- Stroke
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots (in your legs or lungs)
- Nerve injury, which may lead to discomfort, weakness, sexual dysfunction, paralysis, and bladder or bowel control issues.
- Adverse reactions to other medications & anesthesia
Patients with specific health issues may have a higher risk. They also differ depending on the type of surgery you choose. Our spine specialist in Bangalore will help you identify the potential complications and find the procedure that is best for your full recovery.
FAQs:
1. Will there be pain after back surgery?
It is normal to have some pain and discomfort post-surgery. The duration and severity of post-operative pain may vary according to the type of surgery and patients’ pain tolerance levels. In simple surgeries, pain may decrease after 2-3 days, while in complex and major surgeries, it may gradually reduce over 2-3 weeks duration. But if the pain persists for some months together, you should consult your doctor.
2. How long will I be in the hospital following back surgery?
Some patients might need time between 1 to 5 days at the hospital post-surgery, again depending on the type and complexity of surgery. Some types of spine surgeries (Endoscopic) can be done as a day-care procedure also.
3. Will I have a scar?
Any surgery will leave a scar. If the surgery is done using a minimally invasive keyhole technique, the scar will be small.
4. How long does it takes to recover from major spine surgery?
Recovery from the surgery also varies according to the type and severity of surgery. While in many surgeries, patients can go back to their routine daily activities in 2 weeks, in some cases and surgeries, it may take 2-3 months. It also depends on the timing of surgery. Patients who undergo surgery in advanced disease stages and after onset of weakness or numbness usually take longer time to recover.
It takes around 3 to 6 weeks to get back to your regular mobility and function.
5. What is the most common spine surgery?
Discectomy and decompression are the most common types of surgery followed by fusion procedure.
The source of information for the FAQs are mentioned below:
https://www.doneurosurgery.com/faqs-about-spine-surgery.html
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/lumbar-decompression-surgery/recovery/
https://orthoexperts.com/most-common-types-of-spine-surgery/