Fatty liver disease is increasingly becoming a global health issue, affecting millions of people worldwide. It develops when fats are deposited in the liver, impairing its activities, which may culminate in dire circumstances if it is not dealt with. In this blog, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, treatment, and how one can prevent himself/herself from developing a fatty liver disease. For specialized care, one can visit a Gastroenterology Hospital in Hebbal Bangalore for expert evaluation.
What is Fatty Liver Disease?
Fatty liver disease, also referred to as hepatic steatosis, is a condition that results from excessive fats being deposited into the liver cells. The liver is normal to have some fat, but it becomes an issue when fat makes up more than 5 to 10 per cent of the total weight of the liver. There are two kinds of fatty liver diseases:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): This is seen in people who drink little or no alcohol at all. It is often associated with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): This is caused when a person takes too much alcohol, damaging the liver and resulting in fat build-up.
What Causes Fatty Liver Disease?
There are a number of factors that lead to the development of fatty liver disease, such as:
- Obesity: Extra body fat leads to an increased possibility of fat storage in the liver.
- Diabetes: Resistance to insulin and subsequently high blood glucose causes fat to accumulate in the liver
- High Cholesterol and Triglycerides: These fats circulate in high concentrations in the blood to cause fatty liver.
- Poor Dietary Habits: High concentrations of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats are deposited in the liver.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of exercise contributes to the deposition of fat in the liver.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: In AFLD, alcohol disrupts the liver's ability to metabolize fat, leading to fat accumulation.
- Genetic Causes: There may be some people who have a genetic predisposition for developing fatty liver disease.
- Certain Medications: Certain drugs, like corticosteroids, as well as chemotherapy agents used over a long time, contribute to fatty liver.
What are the Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease?
The early stage of the disease is mostly asymptomatic. Thus, diagnosis might be a little challenging at this stage. Advanced stages might also present the following symptoms:
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pain in the abdomen, specifically in the upper right abdomen
- Weakness
- Liver enlargement
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes in severe cases)
If a fatty liver becomes more severe and reaches a stage like non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) or liver cirrhosis, there may be other symptoms that appear, such as swelling in the abdomen, confusion, and internal bleeding.
Risk Factors for Fatty Liver Disease
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing fatty liver disease, including:
- Obesity and being overweight
- Type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance
- Metabolic syndrome (a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Sleep apnea
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
- High blood pressure
- Rapid weight loss
Are there any Complications for Fatty Liver Disease?
If left untreated, fatty liver disease can progress to more severe conditions such as:
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A more advanced form of NAFLD that includes liver inflammation and damage.
- Liver Fibrosis and Cirrhosis: Persistent liver damage can lead to scarring (fibrosis), which, over time, may progress to cirrhosis—a serious, irreversible condition.
- Liver Failure: End-stage liver disease requiring transplantation.
- Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Fatty liver disease is linked to heart disease and stroke.
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease is often diagnosed through a combination of:
- Medical History and Physical Examination
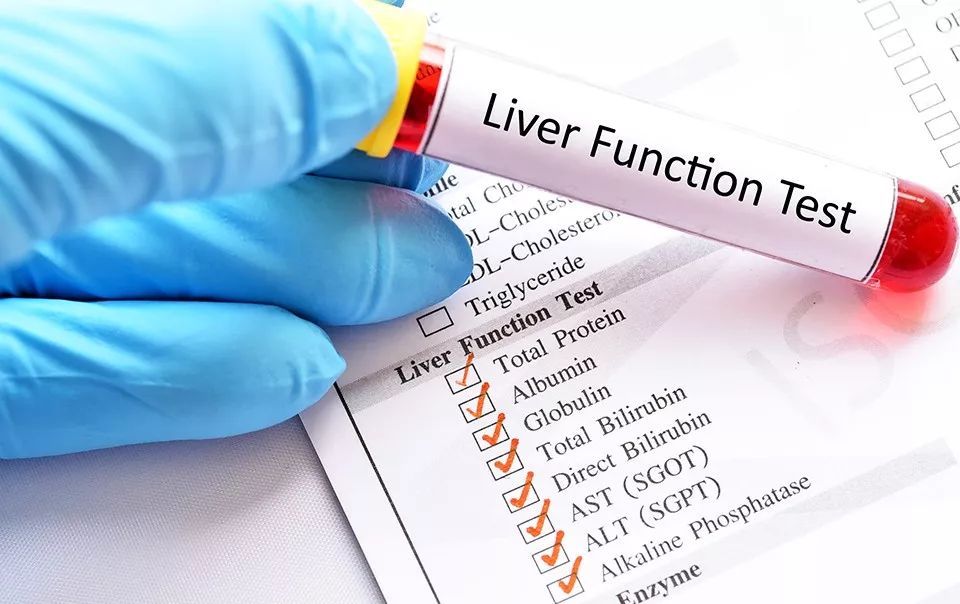
- Blood Tests: Liver function tests (LFTs) to check enzyme levels.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to detect fat accumulation in the liver.
- Liver Biopsy: In some cases, a small tissue sample may be taken to assess liver inflammation and damage.
Consulting with experienced Gastroenterologists in Hebbal Bangalore can help ensure accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.
How to Treat and Manage Fatty Liver Disease?
Unfortunately, there is no specific drug that cures fatty liver disease right now. However, one can easily manage and reverse the condition through a change in one’s lifestyle:
1. Weight Management
Losing 5-10% of body weight can significantly reduce liver fat and inflammation. This can be achieved through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
2. Healthy Diet
- Increase fiber intake: Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables help improve metabolism and reduce fat accumulation.
- Choose healthy fats: Opt for sources like olive oil, avocados, and nuts instead of saturated and trans fats.
- Reduce sugar and refined carbs: Avoid sugary drinks, white bread, and processed snacks.
- Increase protein intake: Lean meats, fish, beans, and legumes support muscle maintenance and overall health.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps with liver detoxification.
3. Regular Exercise
To remove liver fat, try to engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercises like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming five times a week.
4. Handling Underlying Conditions
Proper care for diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol can stave off progression of fatty liver disease.
5. Avoiding Alcohol and Harmful Medications
For individuals with AFLD, quitting alcohol is essential for preventing further liver damage.
Prevention of Fatty Liver Disease
Preventing fatty liver disease involves making long-term lifestyle changes, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Eating a nutritious, well-balanced diet
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Managing underlying health conditions like diabetes and hypertension
- Avoiding unnecessary medications that may harm the liver
When to Consult a Medical Professional
It is necessary to see a doctor if you have fatigue that lasts long, weight loss with no clear reasons, yellowing of skin or eye, and soreness around your abdomen. Bear in mind that early identification of the liver ailment and changing some habits can eliminate dire consequences.
Summary
Fatty liver disease is not only widespread but it can also be easily avoided with some lifestyle modifications. A balanced diet, frequent physical activity, and controlling one's body weight are all extremely important in minimizing, and even eliminating, fatty liver disease. Such lifestyle decisions can come in handy as a shield for the liver and the person’s general health too.
By taking care of your health now, you can stave off the possibility of severe complications later on. Changes such as diet and exercise are small but carried out diligently, these changes can translate to better liver function and general well-being. Preventative checkups and care can diagnose fatty liver disease before it has the chance to progress to worse stages. Liver health is pivotal hence it needs to be taken seriously, and this will lead to a better age expectancy.