The world of cardiac sciences has seen groundbreaking advancements over the past decade, and one of the most revolutionary innovations in recent times is the leadless pacemaker. Compact, efficient, and minimally invasive, these devices are redefining how we manage certain types of heart rhythm disorders, particularly bradycardia (a condition where the heart beats too slowly).
What is a Pacemaker?
A traditional pacemaker is a small device implanted under the skin, usually near the collarbone, with wires (called leads) that extend into the heart. These leads deliver electrical impulses to help regulate an abnormal heart rhythm.
While traditional pacemakers have saved countless lives, they come with certain risks and complications—such as infections, lead displacement, or lead-related damage to heart tissue.
Enter the Leadless Pacemaker
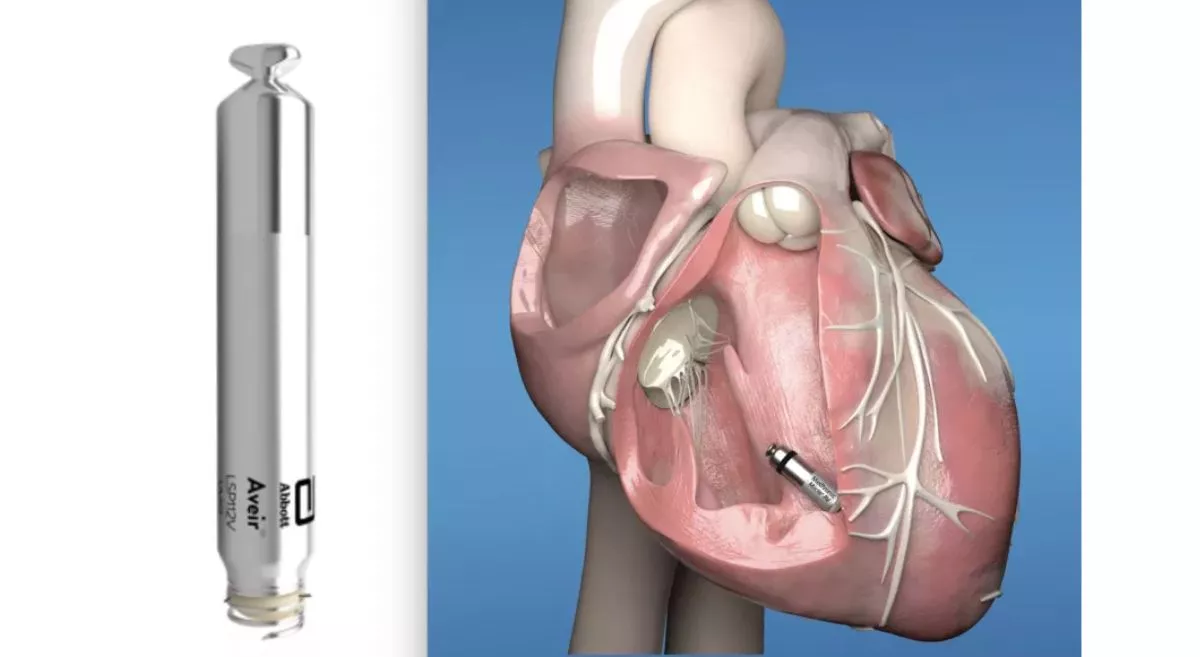
Leadless pacemakers are tiny, capsule-sized devices (about the size of a large vitamin pill) that are implanted directly into the heart’s right ventricle via a catheter inserted through a vein in the groin. Unlike conventional pacemakers, they require no leads and no surgical pocket under the skin, eliminating many of the complications associated with traditional systems.
Why Are Leadless Pacemakers a Technological Marvel?
- Minimally Invasive Procedure
The implantation of a leadless pacemaker typically takes under an hour and doesn’t require open-chest surgery. The entire procedure is done via a catheter-based approach, significantly reducing recovery time.
- No Leads, No Pocket
Traditional pacemakers need a pulse generator placed under the skin and one or more leads threaded into the heart. Leadless pacemakers, being self-contained, eliminate these components—removing risks such as lead fracture, insulation failure, or pocket infection.
- Reduced Complications
Clinical studies have shown that leadless pacemakers significantly reduce device-related complications compared to traditional systems, especially in elderly or high-risk patients.
- Long Battery Life
These devices are engineered for durability and typically last 10-15 years. Some even come with features that automatically adjust pacing based on the patient’s activity level.
- MRI Compatibility & Remote Monitoring
Many models are MRI-safe and offer remote monitoring, allowing physicians to keep track of heart health without frequent hospital visits.
- Improved Aesthetic and Comfort
With no surgical scar on the chest or visible bump from a device pocket, patients often prefer leadless pacemakers for cosmetic and comfort reasons.
Who is a Candidate for a Leadless Pacemaker?
While this innovation is ideal for many patients, it is currently best suited for those who:
- Require single-chamber ventricular pacing.
- Are at high risk for infections.
- Have limited venous access or have had lead-related complications in the past.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Cardiac Pacing
With ongoing research and development, we can expect future versions of leadless pacemakers that support dual-chamber pacing and even wireless communication between multiple devices. This opens the door to more complex rhythm management while maintaining the advantages of a leadless system.
Advanced Heart Care at Aster CMI Hospital
At Aster CMI Hospital, Bangalore, we are proud to be at the forefront of cutting-edge cardiac technologies, including leadless pacemaker implantation. Our team of highly experienced cardiologists and electrophysiologists is equipped with the latest tools and training to offer the safest and most effective treatment options tailored to each patient’s unique needs.
Whether you're seeking a second opinion or advanced cardiac care, Aster CMI ensures clinical excellence with compassion—helping hearts beat stronger, longer, and healthier.