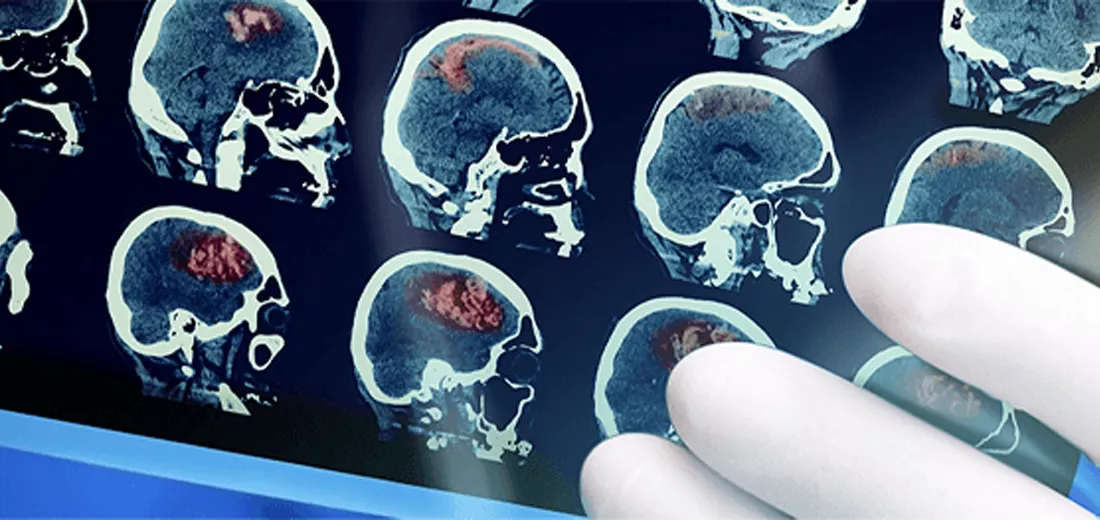
A brain tumour is a mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain. Many brain tumours can disrupt the functions of brain. Others however, are less harmful. Brain tumours are either malignant or benign. By definition, malignant tumours are more aggressive than benign tumours.
Benign tumours doesn’t have cancer cells. They grow slowly and tend not to spread from original site. They are more common than malignant tumours.
Malignant tumours contain cancer cells and don’t have clear borders. They can grow rapidly and spread to other parts of brain, which makes them more dangerous. Tumours are based on the site from which the cells originated. If tumour began in brain, it is a primary brain tumour. If it began in another part of the body and spreads to brain, its called secondary (metastatic) brain tumour.
Each type of tumour has a range of different characteristics and subtypes, and a tumour may consist of more than one type of cell.
Symptoms of brain tumor:
Symptoms vary depending on type of tumour and its location. The following symptoms may occur slowly and gradually get worse. They may also develop quickly in the form of a sezuire (fits).
Common symptoms include:
- Persistent headaches
- Problems with vision
- Seizures
- Issues with short term memory
- Speech problems
- Coordination issues
- Personality changes
- However some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
Diagnosis for brain tumor:
To diagnose a brain tumour, we may carryout a neurological examination. During this examination, we will check various functions for problems with possible links to a brain tumour.
These include:
- Limb strength
- Hand strength
- Reflexes
- Hearing
- Vision
- Skin sensitivity
- Balance
- Coordination
- Memory
- Mental agility
After these tests, we may then schedule additional tests, including:
CT scan: this produces a detailed x-ray image of brain
MRI scan: this uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to provide a detailed image of the brain
EEG : during this test, a healthcare professional will attach electrodes to the person’s head to check for any abnormal brain activity.
If we suspect a brain tumour, we may advice for a tissue biopsy. During a biopsy, a piece of tumour is removed and then send for laboratory testing. The tests aim to identify whether or not the tumour is cancerous.
Risk factors:
Most brain tumours do not have links to any known risk factors. The only known environmental risk factor for brain tumour is exposure to radiation, usually from radiation therapy for other cancers. Also most people with brain tumour donot have a family history of the condition. However, some familial cancer disorders cann contribute to certain types of brain tumours. These include:
Neurofibromatosis 1 and 2
Tuberous sclerosis
Von hippel-lindau disease
li-fraumeni syndrome
people with weaker immune systems, such as those with late stage HIV, might also have an increased risk of brain tumours.
Treatment:
There are several factors that are considered when deciding how to treat brain tumours. We will work closely with the patient to inform them of their treatment options, which will allow them to choose the most suitable treatment.
Factors that are considered include:
- The persons age
- General health status
- Medical history
- Location, size and type of tumour
- Risk of the tumour spreading
- Person’s tolerance for certain treatments
The following are some of the most common treatment methods for brain tumour.
Surgery
Surgery is usually the first method of treatment for brain tumours. Aim will be to remove as much of the tumour as possible. We will try to do so without damaging anyof the healthy brain tissue that surrounds the tumour.
Sometimes, surgeon may not be able to remove the entire tumour. If this is the case, they may surgically remove as much of it as possible before using radiation or chemotherapy to remove the rest. It is important to note that surgery is not effective against tumours that have soread across a wide area of brain tissue.
Surgery also help provide a tumour sample for biopsy or to relieve symptoms such as pressure on the brain.
Radiation therapy
The aim of radiationg therapy is to destroy a brain tumour or prevent its growth. To do this, healthcare providers will administer beams of intense energy to the patients brain from an external source. This causes the tumour to shrink. The patients immune system then takes action on destroyed cells.
However , radiationg cannot distinguish between tumours cells and healthy cells. It cam damage both types. Different forms of radiation therapy can reduce damage to healthy tissues.
Radiation surgery
This is common name for stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS). This a specialized form of radiation therapy and is not a surgical procedure. SRS allows healthcare provider to administer a precise dose of radiation in the form of an x-ray beam. They can focus the radiation only on the area of the brain where tumour is present. This reduced the risk of damage to healthy tissue.
Other medications
We may prescribe medications like steroids, which donot directly treat tumour, but help with some symptoms and discomfort. Antiseizure medications can help in reducing seizure activity. Also, if a tumour is affecting the function of the pituitary gland, person may need hormone supplements.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy entails the use of specific drugs to treat brain tumours. These drugs stop the brain tumour from growing and work by preventing the tumour cells from duplicating. However, many chemotherapy drugs cannot cross the blood brain barrier and would be unlikely to reach a brain tumour. People with some brain tumours may benefit from the administration of chemotherapy drugs into CSF ( cerebro spinal fluid). However, chemotherapy is prescribed to support surgery or radiation therapy.
Once a brain tumour is diagnosed, the way to go ahead is to have a combined discussion with neurosurgeon and patient relatives, to find the best treatment possible.