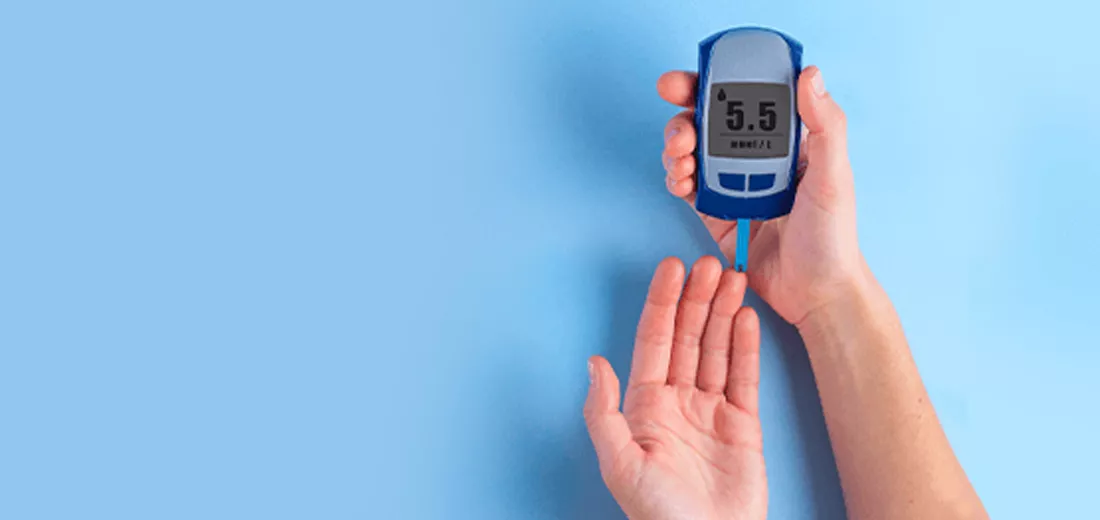
Diabetes is now a major health challenge of the 21st century affecting over 400 million in the world. The prevalence of diabetes across the globe among adults over 18 years of age has increased from 4.7% in 1980 to 8.5% in 2014. Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a global epidemic and India has the second largest population with diabetes in the world. Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of disorders with hyperglycemia [ high blood glucose] caused by a complex interaction of genetics and lifestyle changes. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to several complications.
It can affect the Nerves (Neuropathy), Kidney (Nephropathy), Heart, Eyes, Feet and other organs. Life threatening infections are twice as much common is those without diabetes.
There are different types of Diabetes:
Diabetes is a chronic, costly, but the largely preventable non-communicable disease (NCD), that is responsible for millions of deaths annually and debilitating complications that lead to loss of productivity years. This not only affects the health of nations but also the world economy. In the era of globalization & changing lifestyles, no country, rich or poor, is immune to the epidemic of diabetes. At present, there are equal numbers of people living with undiagnosed type 2 diabetes likely to end up with complications before the detection of their illness. It is therefore important that ongoing diabetes education and support be accessible to all people with diabetes and their families to reduce the impact of the disease on quality of life.
Further diabetes is also increasing among children & young adults. Currently, children with type 2 diabetes mellitus are usually diagnosed above the age of 10 years and in teens. Nearly 30% of India’s teenagers are obese, nearly twice the number in 2010, according to health ministry statistics. The increase in obesity in children and adolescents has been the most important reason for the emerging incidence of diabetes in children. Hormonal changes during puberty coupled with obesity are playing a major role. The children would usually have obesity, increasing waist circumference and darkening of the skin around the neck and axilla, a sign of insulin resistance. In the severest form, the child presents with polyuria, polydipsia, and weight loss.
Diabetes education is the key to self-management of diabetes-related problems. It is essential to make Family members aware of the increasing health burden and economic dimension of the obesity epidemic is of importance. Prevention and treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in youth should become one of the prime targets of public health intervention programs. If you have diabetes in your family, learn about the risks, the warning signs to look out for and what you can do to prevent diabetes and its complications. Many cases of type 2 diabetes can be prevented by adopting a healthy lifestyle. Reducing your family’s risk starts at home. When a family eats healthy meals and exercises together, all family members benefit and encourage behaviours that could help prevent type 2 diabetes.
If you have any of the following risk factors it is recommended to get your blood glucose levels tested.
Type 1 Diabetes (previously known as insulin-dependent, juvenile or childhood-onset): T1DM:
Type 1 Diabetes is due to lack of insulin production by the pancreas and patients need to take daily insulin not just for managing blood glucose, but also for survival. Unfortunately, it is not preventable with current knowledge. The good news is that the availability of modern Insulins (human and analogue) has become a boon to those with T1DM.
Type 1 diabetes is common in children and its prevalence is more than 3 lakhs for the South-East Asian Region including India. The management of TYPE-1 DIABETES is a challenge to all and indeed, not only needs special attention but also extra time and energy to be spared by both healthcare team and family. Today, diabetes being such a common condition, to say that “you have diabetes” is probably OK, but to say “you need insulin lifelong (or You have Type 1 Diabetes)” would seem like a HUGE BURDEN. The management of Type 1 diabetes is indeed a journey that has to be travelled by both the doctor and those with diabetes. It also demands the need for establishing a partnership to set and develop common goals.
The common goals are two-fold: medical and social
Medical: Never ketoacidosis, no severe hypoglycemia with good glycemic control i.e. HbA1c < 7-8 % along with delaying/preventing all the diabetes complications [micro/macrovascular]
Social: Education [ school/college], Marriage & kids and work with the ability to travel freely without fear
We believe that the progress in the management of diabetes care stands on two important ”pans” of the ”balance scale” and the role of a care provider is to ensure that the pivot is able to balance them equally.
1. Social network, motivation and support
2. Understanding own physiology and hence the management [insulin]
REMEMBER THESE LINES:
“You are one among us and it’s not your fault”
“Your goal is your motivation and you can do it”- “Accept Less pain, for more gain”
“Insulin is a must for life”& “Insulin gives you the energy to achieve your goal”
“Eating is essential, but remember taste is not everything”
Type 2 – Diabetes- In this condition, less insulin is secreted or insulin secreted by our body does not work the way it has to work because of resistance to Insulin action
Type 1- Diabetes- Where there is little or no insulin secreted in our body leading to life-threatening emergencies (DKA: Ketoacidosis)
Gestational Diabetes - Diabetes (or Glucose intolerance) that occurs or is detected for the first time during pregnancy
Other rare forms: Secondary, Pancreatic, MODY etc
Family member is having diabetes (Mother, father, brother, sister)
You were found to have Pre-Diabetes during routine testing
You are overweight or your waist circumference is more than 90cms(male) or more than 80cms (female)
You have had diabetes during pregnancy or if your baby weighed more than 4kgs at birth
You are having polycystic ovary syndrome
You have high blood pressure or abnormal cholesterol levels [ especially high triglycerides with low HDL
If you are older than 45 years, it is recommended to get your blood sugar level tested even if you do not have any risk factors
- “Any food we eat has the capacity to increase blood glucose but the rise depends on the type of food-SO CHOOSE WISELY”
“Exercise – activity reduces blood sugar”
“Being active gives you strength and keeps the mind fresh”
“Check sugars and move ahead in life”
“Understand the glucose variations with insulin, food and activity”
Hence Eat Healthy, Be Active and Think Positive, and never forget to check blood glucose or take insulin.