World Diabetes Day is celebrated every year on 14th November, and such a date reminds the world about the rapidly rising diabetes epidemic and its consequences on people. The day was instituted in 1991 when the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the World Health Organization (WHO) became increasingly concerned about diabetes. Today, it has become the world’s largest diabetes awareness campaign, and nearly one billion people in 160 countries across the globe are aware of this issue. Every year, World Diabetes Day has a different theme, and the theme for this year is "Diabetes and Well-being." The Society for Metabolic Health and Weight Management devised this theme as it aims to deliver information on healthy ways of managing diabetes and promoting well-being whilst emphasizing overall health.
Diabetes and its types:
Diabetes, a complex condition that is becoming more common all over the world, is a chronic medical illness that occurs when blood glucose (sugar) levels in the body are too high. Cells in the body require glucose as nutrition; however, in those who have diabetes, glucose remains in the circulation rather than being absorbed by the cells. Diabetes has three main types:
Type 1 Diabetes: Largely occurring in children or young people, this condition is a type of autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks cells in the pancreas which are responsible for the production of insulin.
Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form of diabetes, often developing in adulthood, though increasingly seen in younger individuals. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it.
Gestational Diabetes: This type only appears during a woman’s pregnancy and generally resolves on its own after the birth of the baby. However, it poses a threat of increasing the chances of developing type 2 diabetes chronologically.
Each form of diabetes has a different effect on the body; however, they have one particular problem, which is their grappling to keep blood sugar levels within their optimal range in the face of any possible complications. Poorly managed diabetes can give rise to life-threatening conditions like heart problems, damage to kidneys, nerve-related issues, and even loss of eyesight.
How is Diabetes and Well-being connected?
The first thing that needs to be understood is that diabetes is not simply about managing sugar levels in the blood or taking medicine without doing anything else. Diabetes is a life adjustment that impacts mental, emotional, and physical well-being. To properly manage diabetes, it is necessary to make several lifestyle changes that will assist in managing it properly. Here’s how diabetes and well-being are interconnected:
- Mental Health and Diabetes
Would you like to consider how badly diabetes can dysregulate the minds of people suffering from this chronic condition? Well, for most people, the onset of diabetes management is a pretty heavy task by itself, and I am not even talking about stress or anxiety that goes hand in hand after the fact. I am talking about the constant need to monitor blood sugar levels, plan meals, manage medications, and forever careful planning in general. This mental strain is referred to as "diabetes burnout," which affects patient motivation to adhere to necessary precautions to treat this disease.
Diabetes and depression have been found to have a link. A study shows that people with diabetes have a 2x higher risk of being depressed compared to the rest of the population. The relationship is known to be bidirectional whereby diabetes can affect mental health and uncontrolled diabetes can worsen the mental health problem.
- Maintaining Physical Activity as Part of Diabetes Disease Management
There is an established impact of diabetes on physical health, but the physical aspect of health must be focused on to disease manage diabetes. Physical activity contributes to lower blood sugar levels, increased body insulin sensitivity, and weight management, which is important for the prevention of complications. Without a physically vigorous lifestyle, a portion-controlled dietary regimen is critical to lowering blood sugar levels and facilitating weight loss.
- Social and Emotional Support
Social support is crucial for people with diabetes, as it offers a network of people who understand the challenges involved. The presence of emotional support by families and friends helps curb the effect of loneliness and may promote adherence to a healthy lifestyle. Social and emotional support also helps build resilience, which is important in the effective management of diabetes and enhancing quality of life.
Managing Diabetes While Prioritizing Well-being
The theme of "Diabetes and Well-being" underscores the importance of a balanced approach to managing diabetes while maintaining overall health and happiness. Here are several key strategies to manage diabetes holistically:
- Focus on a Balanced Diet
A healthy diet is fundamental for managing diabetes and promoting well-being. The main goal is to maintain steady blood sugar levels without feeling deprived. This includes:
- Carbohydrate Counting: Monitoring carbohydrate intake helps keep blood sugar levels stable. Complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables are preferable as they release glucose gradually.
- Portion Control: Eating moderate portions prevents blood sugar spikes. Small, balanced meals throughout the day help maintain energy and prevent extreme blood sugar fluctuations.
- Including Fiber: Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains slow down glucose absorption and help maintain stable blood sugar levels.
A balanced diet not only aids in managing diabetes but also boosts mood, energy levels, and physical health, contributing to overall well-being.
- Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to manage diabetes and support physical and mental well-being. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week has numerous benefits:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Exercise helps the body use insulin more efficiently, which is especially beneficial for those with type 2 diabetes.
- Weight Management: Physical activity aids in maintaining a healthy weight, reducing the risk of complications.
- Stress Relief: Exercise promotes the release of endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress.
Physical activity can take many forms, from brisk walking and swimming to yoga and strength training. For people with diabetes, it’s essential to check blood sugar levels before and after exercise to avoid hypoglycemia.
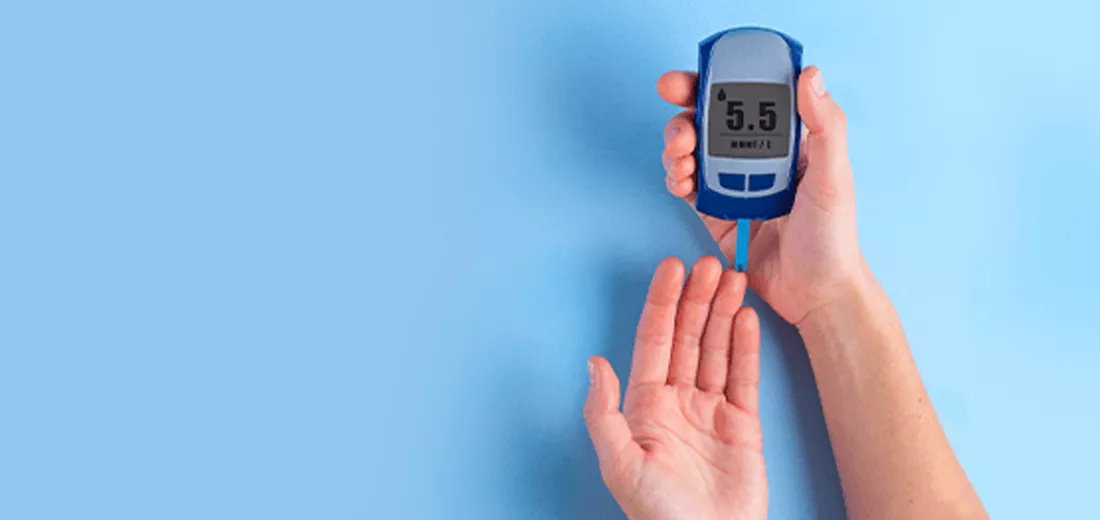
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Keeping track of blood sugar levels helps individuals with diabetes understand how their body responds to food, exercise, and medication. Self-monitoring empowers people to make informed decisions and adjust their routines as necessary. This sense of control can reduce stress and anxiety around diabetes management.
Technology, such as continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), has made monitoring more accessible. CGMs provide real-time blood sugar data, helping individuals make proactive adjustments to their diet and lifestyle. Tracking blood sugar levels can increase awareness and confidence, enhancing well-being.
- Prioritizing Mental Health
Mental health is a cornerstone of well-being for individuals with diabetes. Managing mental health effectively can lead to improved diabetes control and a higher quality of life. Strategies for maintaining mental health include:
- Seeking Support: Talking to friends, family, or support groups can alleviate feelings of isolation and provide practical advice on managing diabetes.
- Mindfulness Practices: Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help reduce stress and increase emotional resilience.
- Professional Help: Therapy, especially cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), can be beneficial for managing diabetes-related stress and depression.
Addressing mental health needs is crucial because it can directly impact the ability to manage diabetes effectively.
- Getting Sufficient Rest
Sleep quality is directly linked to blood sugar control. Poor sleep increases insulin resistance and makes blood sugar hard to manage. It also tends to increase stress and lower energy, making it complicated to follow through on a diabetes management plan. Good sleep hygiene, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, reducing screen time before bed, and creating a calming bedtime routine, will improve diabetes management and general well-being.
Here are some Global Initiatives to Manage Diabetes and Ensure Better Well-being
World Diabetes Day brings global attention to efforts put forth for the well-being and care of individuals afflicted with diabetes. Efforts include measures at the national levels undertaken by the IDF, WHO, and others regarding strategies that can be followed to enhance awareness and to improve accessibility to resources, along with lifestyle changes for the prevention and management of diabetes.
It is very essential to educate people of underprivileged communities through diabetes programs so that they can overcome diabetes-related information. Governments and healthcare systems are also working to make diabetes treatments, such as insulin and glucose monitoring devices, more accessible and affordable.
Conclusion
This World Diabetes Day serves as a reminder that diabetes management is not solely about controlling blood sugar; it’s about ensuring a balanced and fulfilling life. Through a holistic approach—including diet, physical activity, mental health, social connections, and global support—individuals with diabetes can maintain well-being while managing their condition effectively.