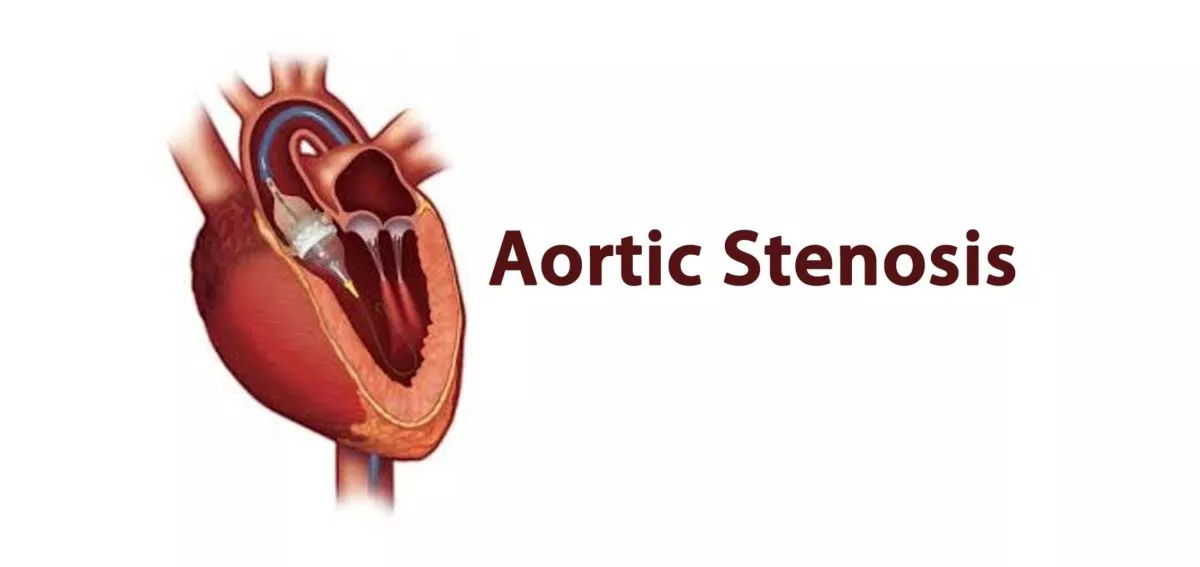
Aortic Stenosis: The aortic valve is located between the heart and the major blood vessel carrying blood out of the heart - the aorta.
Aortic stenosis occurs when the valve narrows and becomes tight preventing blood from smoothly passing out of the heart to the body, Feeling faint, woozy, weak, or unsteady. In older people it may be due to age related changes (senile calcific aortic stenosis) or in middle aged people it may occur in those people with two leaflets in the aortic valve - bicuspid aortic valve.
The main symptoms are shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness and in some cases loss of consciousness. These if ignored over a period of time cause a burden on the heart and lead to heart failure. The diagnosis is made on the basis of symptoms and a few tests - principally an echo.
Aortic stenosis is treated with aortic valve replacement. The Heart Team - you, your medical team, and your cardiothoracic surgeon - will determine the best treatment option for you based on your symptoms and test results. The options range from:
- Conventional aortic valve replacement
- Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement - currently offered to most patients
Advantages:
- Earlier recovery and return to normal activity
- Minimal need for blood transfusion
- Lesser chance of infection
What is Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR/TAVI)
TAVR/TAVI s a form of minimally invasive surgery that does not require opening the breastbone. It is meant for those considered too fragile to undergo regular or minimally invasive aortic valve replacement and is currently the gold standard for these patients
Ask your Doctor about
- Choice of valve for replacement
- Future directions
- Management of small aortic annulus/ root