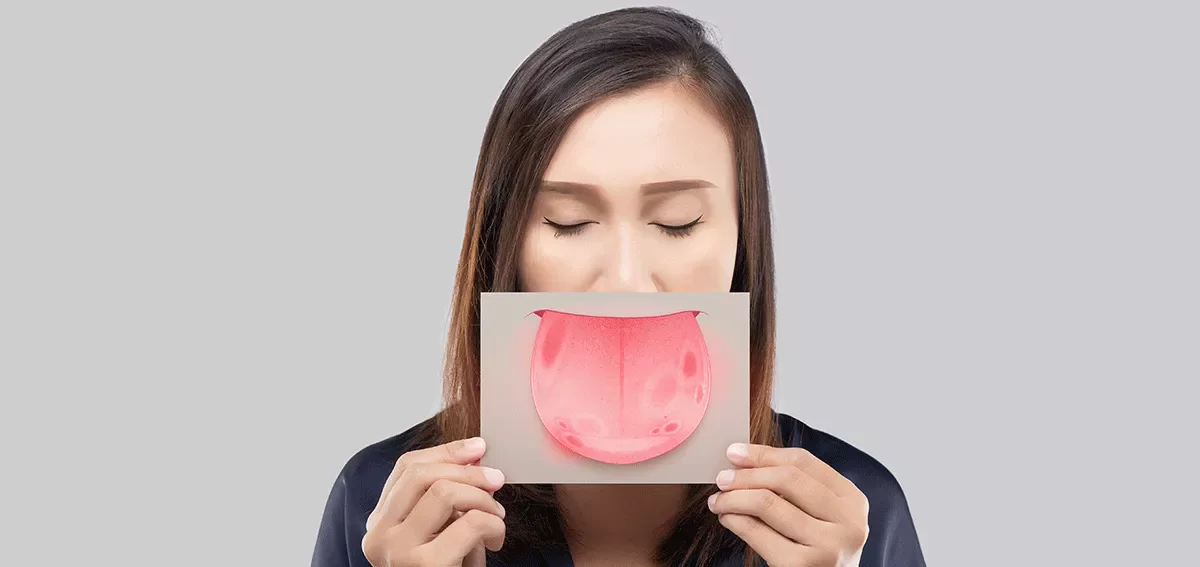
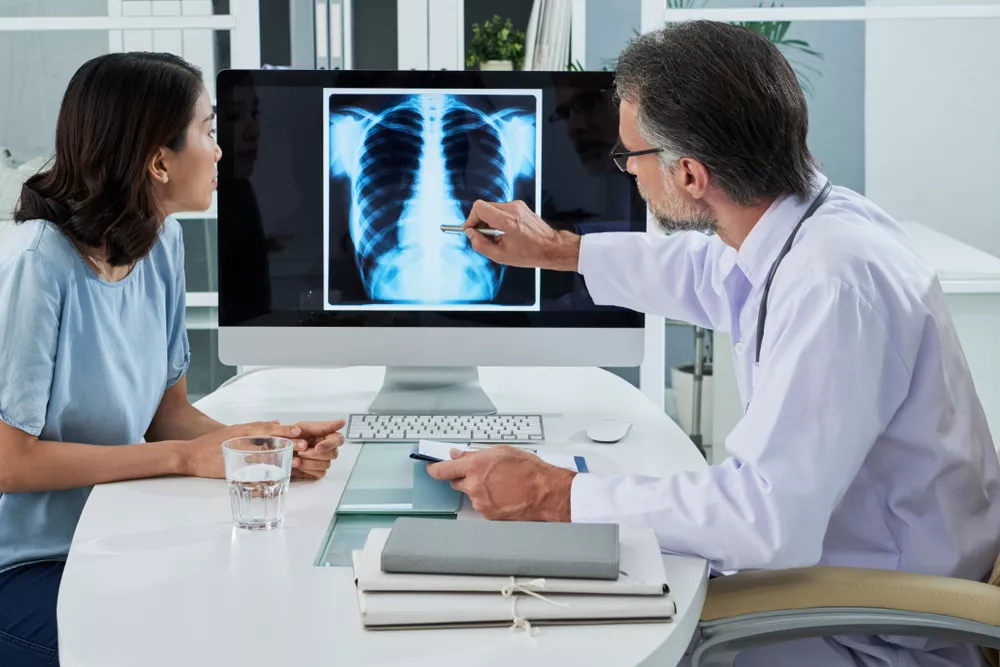
Oral cancer affects several people each year, of which a large percentage is men. Early detection makes treating oral cancer considerably easy for doctors. Patients will have a far higher chance of receiving an early diagnosis if they visit the best cancer hospital in Kerala and learn to recognise any sudden changes. If it is not identified and treated right away, oral cancer could turn fatal.
What is oral cancer?
Any cancer that appears in any part of the mouth is referred to as mouth cancer. Cancer that develops in the cheeks, tongue, floor of the mouth, hard and soft palates, lips, sinuses and throat are all considered a type of oral cancer.
Oral cancer is one of the types of cancer that is included in the neck and head cancer category. Treatment for neck and head cancer and oral cancer is mostly the same.
What is the cause of oral cancer?
Cancer develops when a genetic alteration in the body causes cells to grow out of control. These faulty cells develop into a tumour as they keep multiplying. The cells may move to different areas of the body throughout time.
The most common risk factors for oral cancer include using tobacco products and drinking alcohol. Other factors include:
- Gum disease
- Epstein-Barr Virus
- Chewing areca palm seed (sometimes called areca or betel nut)
- Human Papillomavirus
- Family history of oral cancer
- Poor oral hygiene
- Sun exposure.
What are the symptoms of oral cancer?
Signs and symptoms of oral cancer can be confused with everyday dental issues or mouth changes. For instance, you can discover patches inside your mouth that cannot be removed with a scraper. These patches could be the early stages of cancer.
Common signs and symptoms include:
- Bleeding sores inside your mouth or on your lips that don't heal in two weeks
- Rough or crusty patches on your lips, gums or mouth's interior
- Spots in your mouth that bleed mysteriously
- Unknown causes of numbness, pain or tenderness on your face, neck or in your mouth
- Difficulty speaking, moving your jaw or tongue or chewing or swallowing
- Sudden weight loss
- Earache.
What are the other symptoms of oral cancer?
The following are all the coloured patches that develop on the lips and throat, which indicate oral cancer:
- Erythroleukoplakia: These are white and red patches.
- Leukoplakia: These are spots on the areas of the mouth or throat that are flat, white or grey.
- Erythroplakia: These are red areas that may be flat or slightly elevated. They might bleed when scraped.
- Constant foul breath.
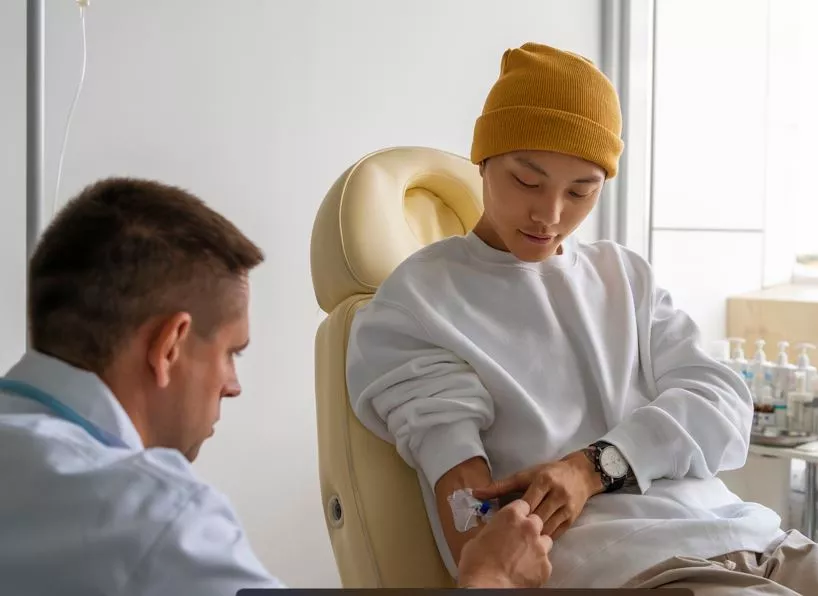
How can oral cancer be treated?
The course of treatment will depend on the patient's overall health; the type, stage and location of their cancer; and their personal preferences. There are several possible methods to treat oral cancer:
Surgery
Oncologists may recommend removing the tumour and any surrounding healthy tissue by performing surgery. The jawbone, lymph nodes and/or a portion of the tongue may also be removed. Reconstructive surgery may be required if the operation dramatically alters the person's appearance, speech or eating abilities.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is effective in treating oral cancer. Applying high-energy radiation or X-ray beams destroys the DNA inside the cancer cells, leaving them incapable of procreating.
Brachytherapy
During the brachytherapy process, the surgeon will administer radiation to the tumour using radioactive needles. This is mostly suggested for patients who have early stages of tongue cancer.
People who do not smoke or who have previously quit smoking will likely respond to treatment more favourably.
Radiation therapy alone might be sufficient for a patient with early-stage mouth cancer, but doctors may advise combining it with additional therapies to lower the likelihood of the disease spreading or coming back.
Chemotherapy involves administering potent medications that harm the DNA of the cancer cells. The medications prevent the cells from proliferating and spreading.
Chemotherapy drugs kill cancer cells, but they may also harm healthy tissue.
These outcomes could include:
- Fatigue
- Dizziness and vomiting
- Hair fall
- A compromised immune system and heightened infection risk.
These side effects generally disappear at the end of treatment procedures.
Immune Targeted Therapy
Cetuximab is a biological medicine that is used to treat advanced cases of oral cancer. It is combined with radiation or chemotherapy.
Cetuximab targets epidermal growth factor receptors, which are proteins on the surface of cancer cells. Cetuximab inhibits cancer from spreading by targeting specific proteins that aid in cancer growth. Pembrolizumab is an immunotherapy that treats melanoma, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma, stomach cancer, cervical cancer, and certain types of breast cancer.