10 year old male child John (name changed) presented with complaints of severe headache followed by loss of consciousness and seizures. Patient was stabilized and relevant investigations and imaging were done. MRI revealed ruptured right side splenial arteriovenous malformation(AVM). He was taken up from cerebral angiogram and angioembolization. Angiogram revealed ~1.5x1.5cm AVM in right side occipital region fed by splenial/posterior choroidal branch of PCA with at-least 3 draining veins into straight sinus. There was suspicious small intranidal aneurysm as well. The feeding branches was selectively catheterised with microcatheter and sequential embolization of the arteriovenous malformation was done with liquid embolic agent. Post procedure there was near total embolization of the AVM with no obvious nidus remnant. Post procedure period was uneventful. Physiotherapy was done. Patinet was discharged in ambulatory condition with no fresh neurological deficits. This case highlights the importance of timely intervention by experienced Neurologists in JP Nagar Bangalore in managing complex neurological emergencies.
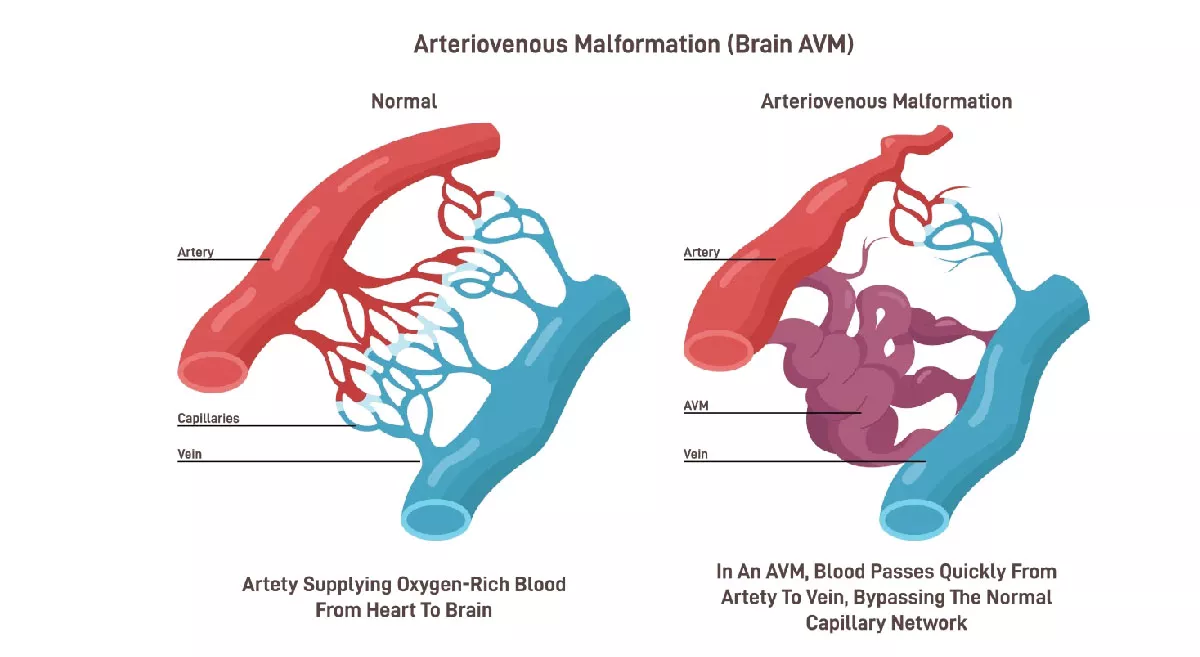
What are arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
Arteriovenous malformations are abnormal communications between arteries and veins forming tangle of blood vessels. These vessels are unable to handle the high flow and pressure of arterieal blood and hence are highly prone for rupture.
What are the common locations of arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) can affect any part of the body. There are broadly divided into brain AVM and other peripheral AVM. Advanced facilities at a leading Neurology Hospital in JP Nagar Bangalore play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating such conditions effectively.
What are the common causes of arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
Most of the arteriovenous malformation (AVM) are congenital and develop during intrauterine period and grow with age. Familial and post traumatic are the other two most common causes.
What are the symptoms of brain arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) of brain present with varied symptoms ranging from headache, intracranial bleed, stroke, seizures, numbness, dizziness, vomiting, behavioral disturbances etc.
How do we diagnose brain arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
Diagnosis is usually done by MRI /CT with angiography. Sometimes, conventional catheter angiography may be required for confirmation of diagnosis.
Is endovascular treatment option available for brain arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
Angioembolization is a minimally invasive surgery/procedure used to treat brain AVM. Vascular access (tiny hole ~2-3mm) is made through an artery in the thigh (femoral artery). Small catheters are super selectively passed into the AVM and blocked using liquid embolic agent. Other options include surgery, radiation or combination of any of the above.
What are the advantages of angioembolization?
- Minimally invasive procedure
- No cuts/ scars/sutures.
- Shorter hospital stay (3-4 days)
- Almost nil requirement for blood transfusion