Introduction
There is a need to raise awareness on radiography’s role in healthcare. The critical significance of radiography and X-ray technology in diagnosing and treating various health conditions, shedding light on the impact these advancements have on patient care is little known to common man. Expertise of radiography professionals is essential in diagnosing injuries, diseases, and conditions; it promotes appreciation for the invaluable contributions to healthcare.
Discovery of X-rays is an invaluable contributions of radiography professionals to healthcare. It has revolutionized medical science, allowing doctors to view internal structures without invasive surgery. It is important for us to educate the public about the technological advances and functional aspects of radiography.
Functionality and Applications of Radiography
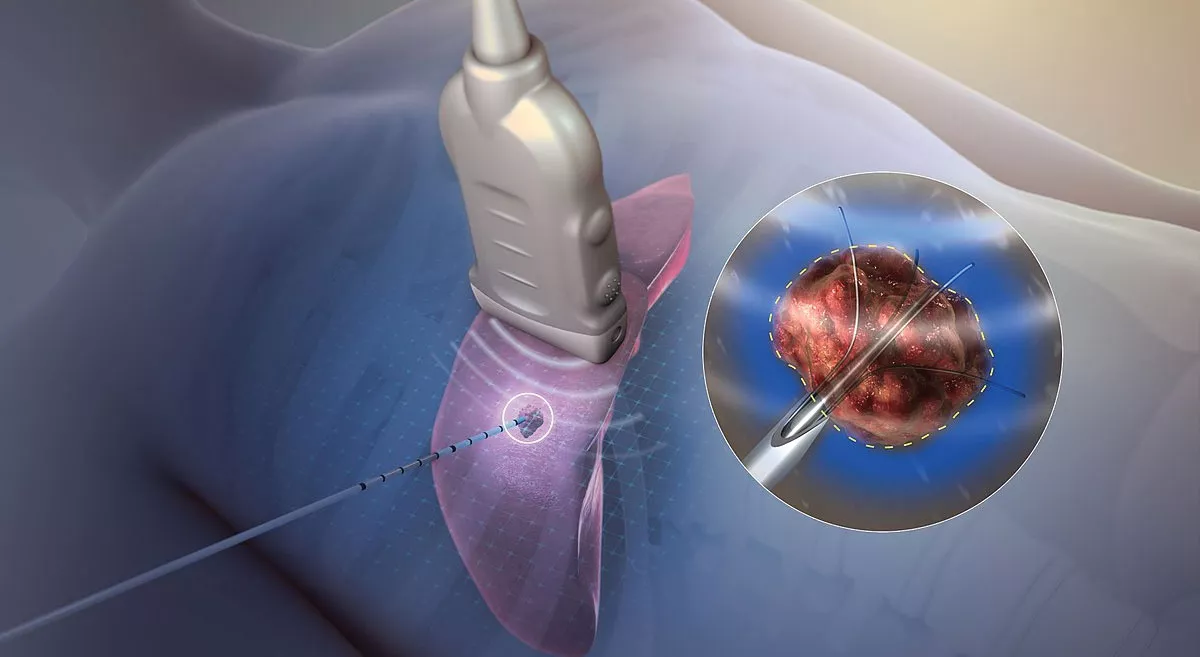
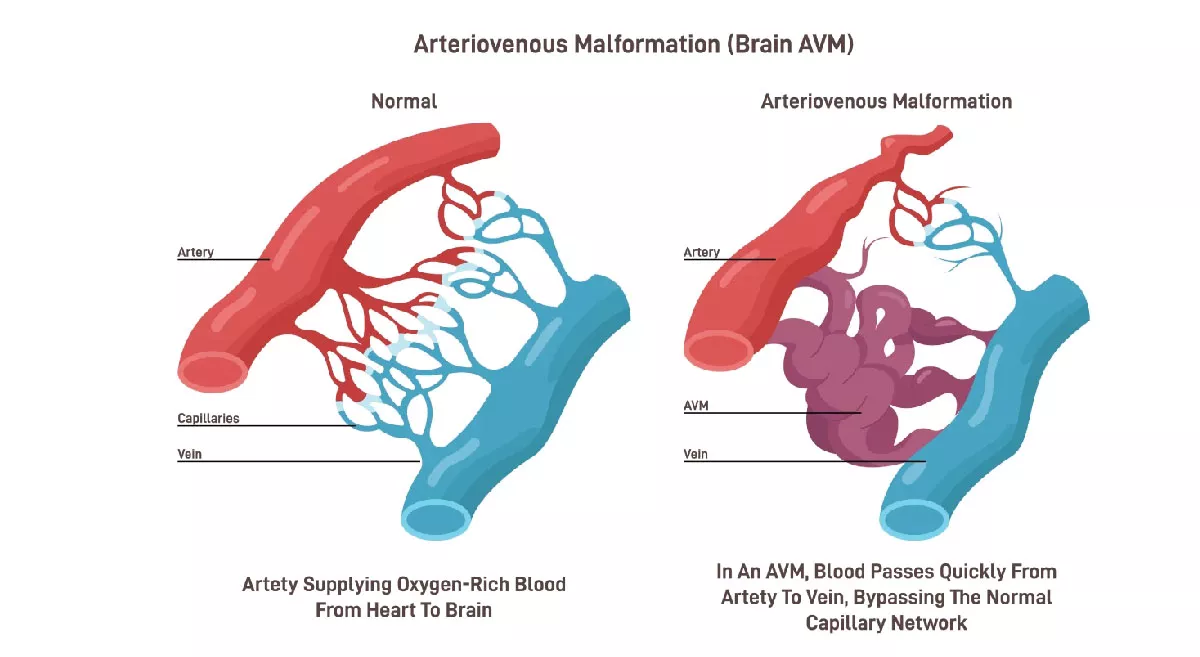
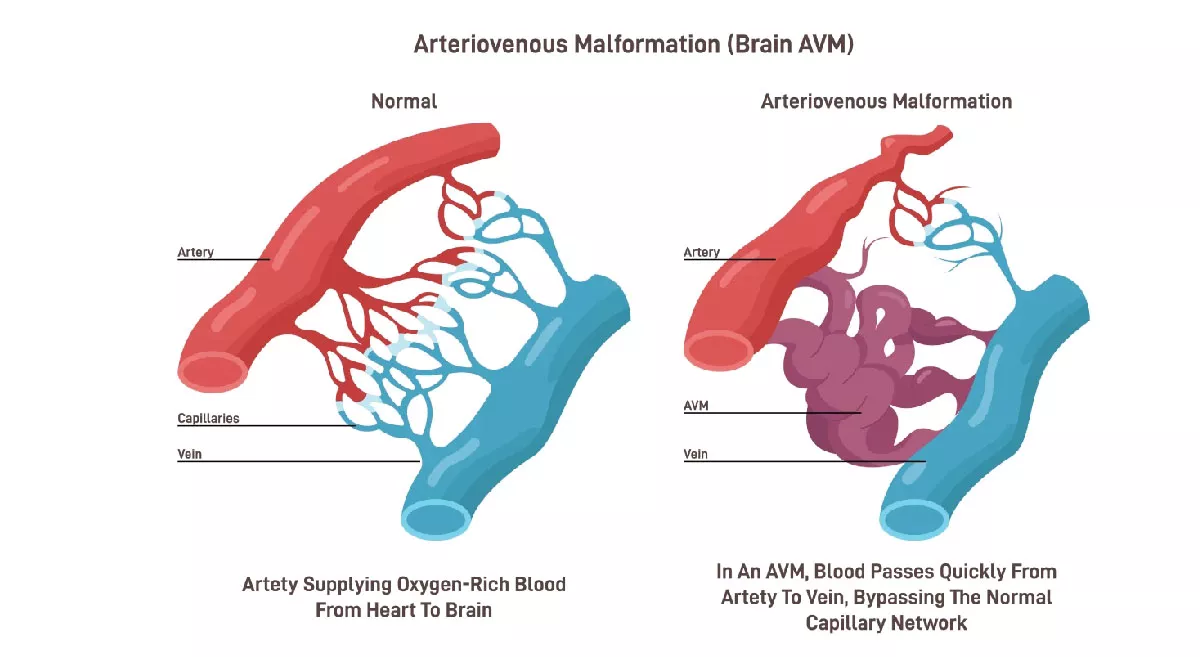
Radiography involves the use of X-rays to visualize internal structures of the body, serving a wide range of medical fields. In diagnostic imaging, X-rays and advanced techniques like CT scans, MRI, and PET scans allow healthcare professionals to diagnose fractures, tumors, infections, and other conditions. Radiography also supports interventional procedures by guiding the placement of catheters, stents, and aiding in biopsies and minimally invasive surgeries. In oncology, therapeutic radiography is critical for planning and delivering targeted radiation therapy to treat cancer while protecting healthy tissue. In dentistry, X-rays help assess oral health, detect cavities, and monitor bone loss, while in veterinary care, radiography is essential for diagnosing various conditions in animals.
Advancements and Trends in Radiography
Radiography has undergone a major advancement, enhancing both diagnostic precision and patient safety. Digital Radiography now enables high-resolution images with reduced radiation exposure and faster processing times, which cuts down on patient wait times. The advent of 3D Imaging, including Cone Beam CT (CBCT) and 3D reconstruction, allows for more detailed views of complex areas, proving invaluable in intricate surgeries and dental procedures. The integration of AI and Machine Learning in radiography has led to improved diagnostic accuracy by helping radiologists detect subtle patterns and anomalies, such as early-stage tumors or fractures. Low-Dose Techniques are becoming central to radiography, focusing on minimizing radiation exposure while still achieving high-quality imaging for patient safety. Portable Radiography Units now allow imaging at patients' bedsides, a development particularly useful in critical care and emergency settings, as well as during the COVID-19 pandemic when mobility and containment were essential. These advancements mark radiography as an increasingly safe, effective, and versatile field.
Importance of Radiography in Healthcare
Radiography plays a crucial role in healthcare, serving as a key tool for early detection and diagnosis of serious conditions, such as bone fractures, infections, and cancers. By identifying these issues at early stages, radiography significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and survival. Treatment planning is also heavily reliant on accurate radiographic imaging, especially in fields like oncology and surgery, where precise visuals of the affected area are essential for crafting effective treatment strategies. Radiography provides a minimally invasive diagnosis option, sparing patients from the physical stress of surgical exploration and allowing for quicker, less painful procedures with reduced recovery times. Additionally, radiographic imaging enables continuous monitoring of patients' health, helping track the progression or remission of illnesses and assess treatment efficacy, such as tumor reduction in cancer therapy. By providing accurate, early, and ongoing insights into health conditions, radiography is integral to effective and patient-centered care.