Causes and Characteristics of Skin Color Loss
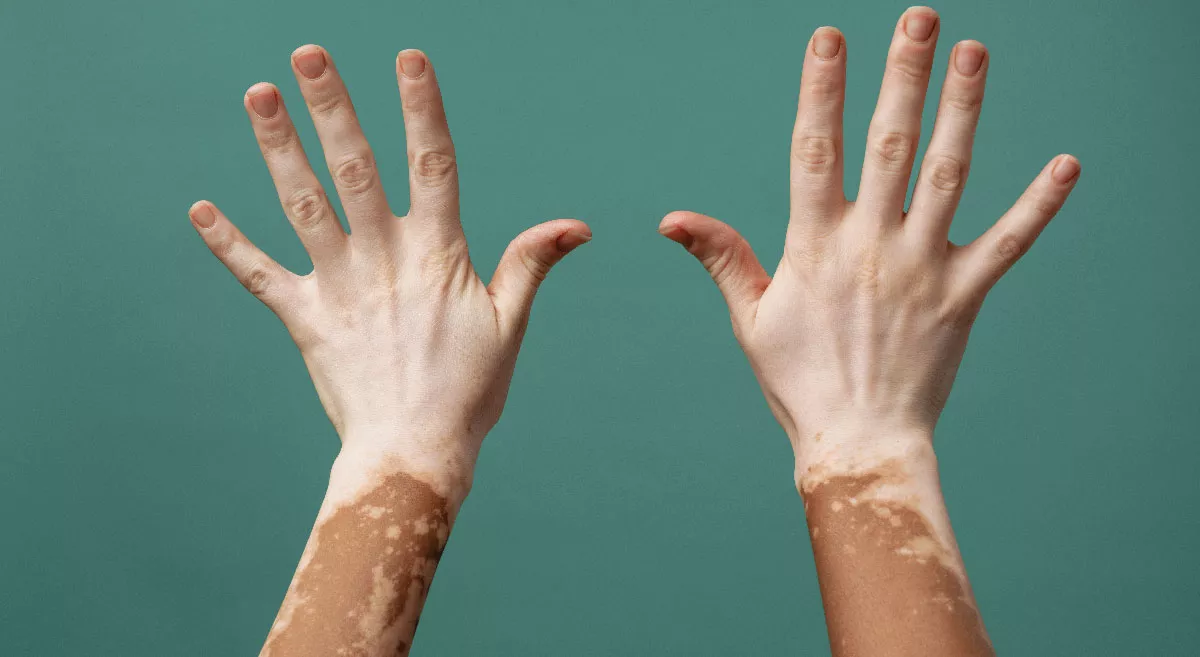
Vitiligo is a condition where it's characterize by the loss of skin color in patches. It occurs when melanocytes (the pigment that gives skin its color), are destroyed or stop functioning. The exact cause of vitiligo believes to involve a combination of genetic, autoimmune, and environmental factors.
Some key points about Vitiligo include:
Symptoms: White Patches in skin. These patches can appear on any part of the body and may affect the hair, inside of the mouth, and even the eyes.
Types: There are different types of vitiligo, including generalized (most common, affecting both sides of the body symmetrically), segmental (affects only one side or part of the body), and localized (limited to one or a few areas).
Causes: It is thought to involve autoimmune factors where the systems attacks melanocytes. Genetic factors and triggers like stress, sunburn, or exposure to certain chemicals may also play a role.
Treatment: It includes topical medications (such as corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors), phototherapy (using UV light), depigmentation (lightening unaffected skin to match vitiligo patches), or surgical options in severe cases.
Psychological Impact: Vitiligo can have significant psychological and emotional effects due to its impact on appearance. Support groups and counseling may be beneficial for individuals coping with vitiligo.
Management: While there is no cure for vitiligo, various treatments can help manage the condition and improve the appearance of the skin. Regular follow-ups with a dermatologist are important to monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
It's essential for individuals with vitiligo to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the best treatment approach based on the type and severity of their condition.