Introduction
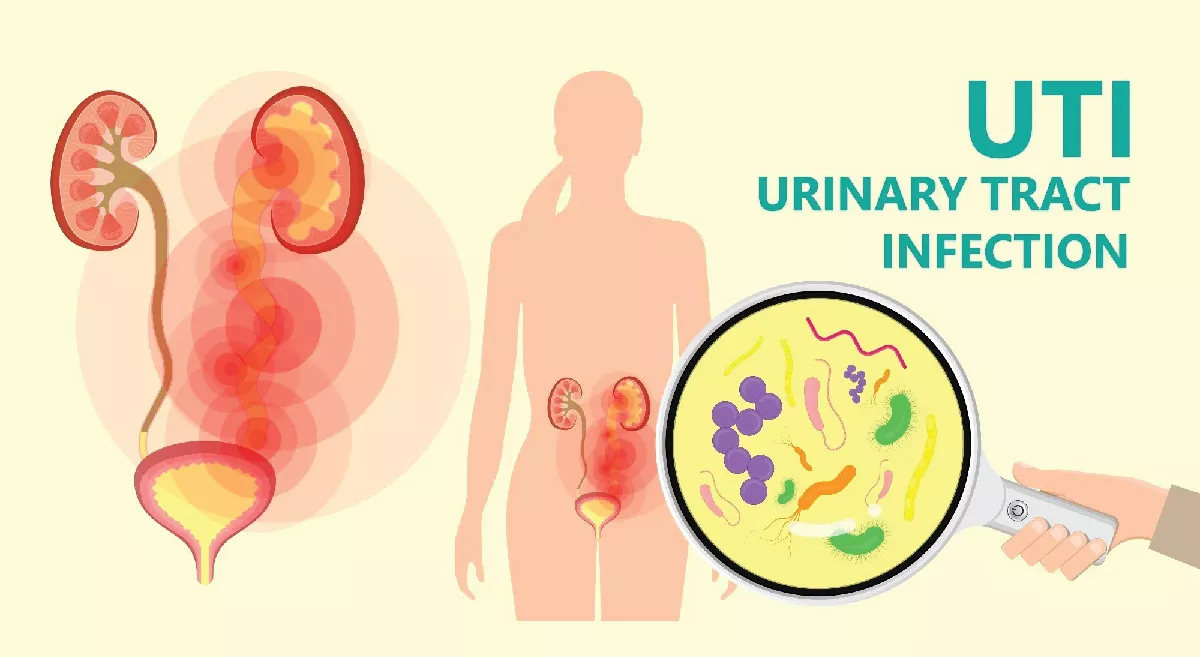
Experiencing pain or a burning sensation while urinating may be a urinary tract infection (UTI). Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections that occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. They are caused primarily by bacteria, though fungi and viruses can also be culprits. UTIs are more common in women due to anatomical differences but can affect men, children, and the elderly as well. Most UTIs can be resolved quickly and effectively when detected early.
Symptoms of UTIs
Common symptoms of urinary tract infections include:
- Urge to urinate frequently, often producing only small amounts of urine.
- Pain, burning sensation, or discomfort while urinating.
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, especially in women.
- Red, brown, or pink urine may indicate blood.
- Fatigue, fever, and chills indicate a more severe infection.
Causes of UTIs
Causes of UTIs include:
- Bacterial infection: UTIs are mainly caused by bacteria like Escherichia coli.
- Sexual activity: Increased risk of UTIs can occur after sexual intercourse.
- Anatomy: Women are more vulnerable to UTIs because they have a shorter urethra, which allows bacteria easier access.
- Urinary retention: The inability to empty the bladder can increase the risk of infection, as residual urine provides a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Catheter use: Urinary catheters can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
UTI Treatment Options
The treatment depends on its severity and location:
- Antibiotics: The primary treatment involves a course of antibiotics (e.g., Amoxicillin, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, etc.) to eliminate the infection.
- Pain relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen can help alleviate discomfort associated with UTIs.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can flush out the infection-causing bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Home remedies: Some individuals find relief using home remedies such as cranberry juice or probiotics, although research on their effectiveness is mixed.
UTI Prevention Tips
Urinary tract infections can be prevented by:
- Drinking sufficient fluids to flush out harmful bacteria.
- Practicing good bathroom hygiene like wiping from front to back can prevent bacteria from spreading.
- Urinating after intercourse can flush out bacteria that may have entered the urethra.
- Limiting irritating products, like scented feminine products.
- Wearing breathable clothing. Opt for loose-fitting cotton underwear to reduce moisture buildup.
UTI Diagnosis
Diagnosing UTI typically involves:
- Medical history: Symptoms like burning sensation, pain, or discomfort during urination, frequency of urination, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and any pain in the lower abdomen or back will be recorded.
- Physical Examination: The abdomen and back is palpated to assess kidney health.
- Urinalysis: A urine sample is tested for bacteria, red blood cells, white blood cells, or nitrites, all of which may indicate an infection.
- A urine culture may be done to identify the infection-causing bacteria.
- Imaging tests (if needed): For recurrent UTIs or a more severe infection, an ultrasound or CT scan may be recommended.
- Cystoscopy (if needed): In cases of chronic or complicated UTIs, a cystoscopy may be performed, where a small camera is inserted into the bladder to examine the urethra and bladder for structural issues.
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections are common but often preventable. By understanding the causes and implementing preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing UTIs and maintain better urinary health. If you experience recurrent UTIs or severe symptoms, please reach out to Aster RV Hospital for further evaluation and management.