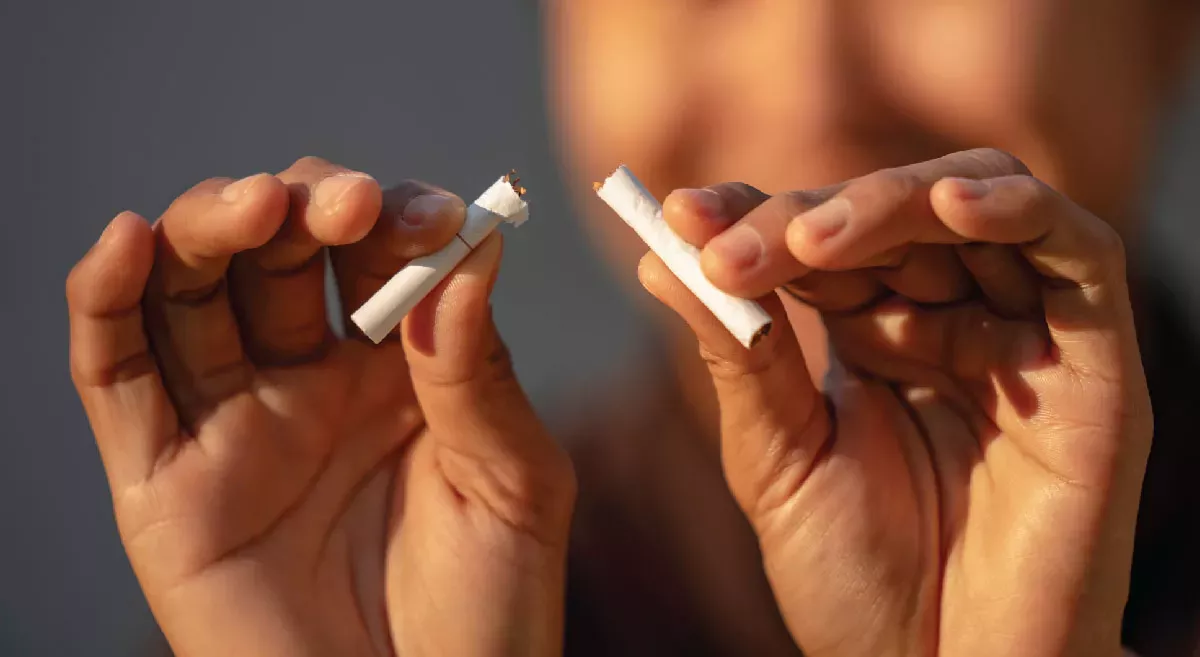
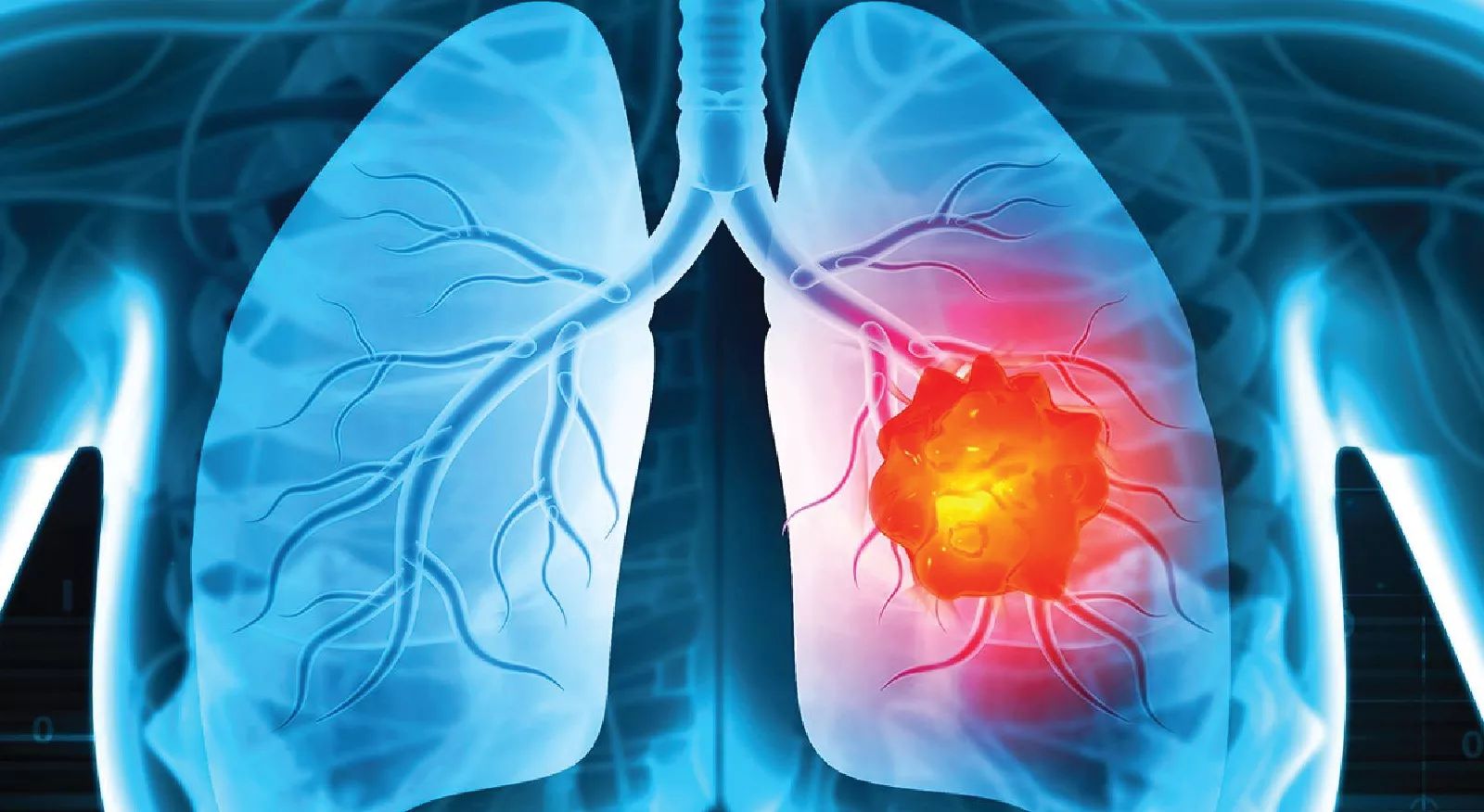
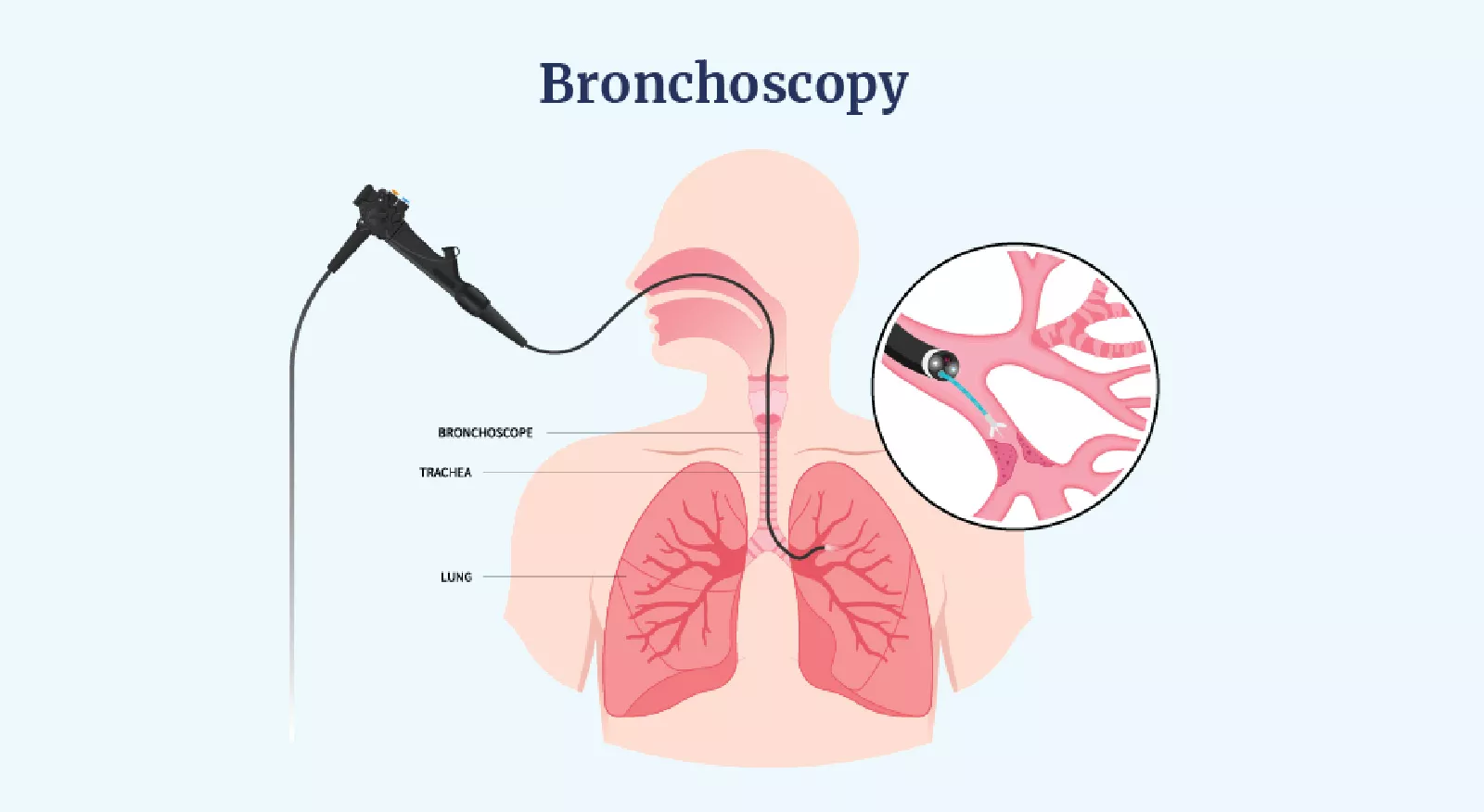
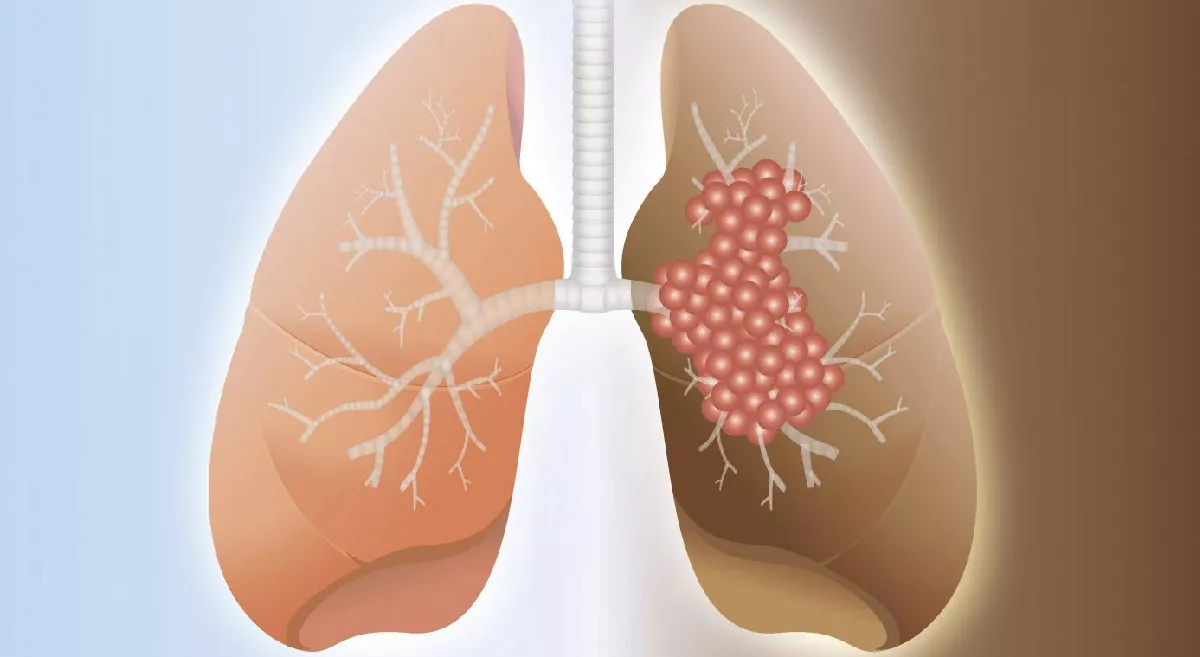
Addressing tobacco addiction requires a multi-faceted approach, incorporating policy interventions, community programs, and individual support.
The following measures are crucial for managing tobacco addiction in India:
Legislative and Policy Measures:
Implementation of the Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products Act (COTPA) 2003:
This legislation regulates advertising, packaging, and sales of tobacco products. Strict enforcement of this act can significantly reduce tobacco consumption.
Taxation and Pricing Policies:
Increasing taxes on tobacco products is one of the most effective ways to reduce tobacco use. Higher prices discourage initiation among young people and motivate existing users to quit.
Public Awareness and Education:
Mass Media Campaigns: Educational campaigns highlighting the dangers of tobacco use and promoting cessation services can influence public attitudes and behaviours.
School-based Programs:
Integrating tobacco education into school curricula can prevent initiation among young people.
Cessation Support Services:
Quit-lines and Helplines: Providing access to quit-lines where trained counsellors can offer support and advice to individuals trying to quit tobacco.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) and Medications:
Making NRT and other cessation aids available and affordable can improve the success rates of individuals attempting to quit.
- Community Engagement and Support:
- Community Health Programs:
Engaging community health workers in tobacco cessation programs can enhance outreach and support at the grassroots level.
Support Groups:
Establishing support groups where individuals can share their experiences and strategies for quitting can provide the necessary social support.
Monitoring and Research:
Surveillance and Data Collection: Regular surveys like GATS help in monitoring trends in tobacco use and evaluating the effectiveness of interventions.
Research on Cessation Strategies:
Conducting research to identify the most effective cessation strategies tailored to the Indian context.
- Conclusion
No Tobacco Day serves as a critical reminder of the ongoing battle against tobacco addiction in India. The country’s high prevalence of tobacco use underscores the urgent need for comprehensive strategies encompassing policy, education, support services, and research. By strengthening these efforts, India can significantly reduce the burden of tobacco-related diseases, improve public health, and save millions of lives.