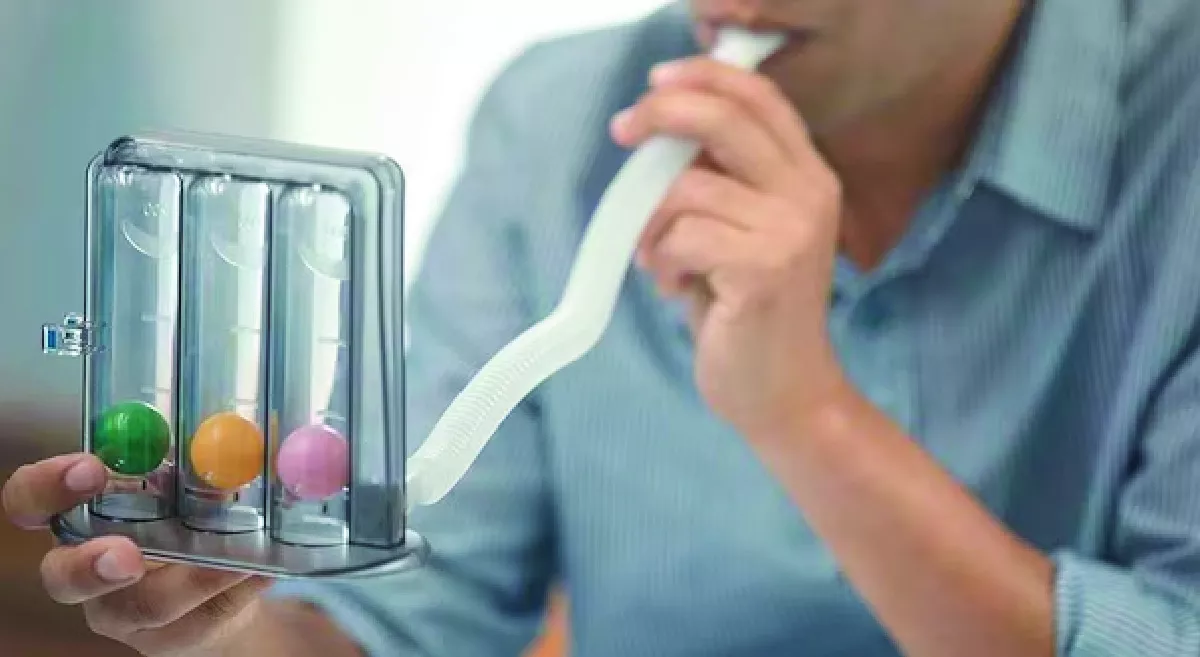
It is typically involves a combination of medications, airway clearance techniques, and management of any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the condition. Below are some examples of medical management options for bronchiectasis.
Medical Management of Bronchiectasis
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are often used to treat bacterial infections in the lungs. In some cases, long-term antibiotic therapy may be needed to prevent recurrent infections.
Bronchodilators
Bronchodilators are medications that help to open up the airways and make it easier to breathe. They may be used to treat symptoms such as wheezing and shortness of breath.
Inhaled corticosteroids
Inhaled corticosteroids can help to reduce inflammation in the airways and may be used to manage symptoms such as cough and shortness of breath.
Mucolytics
Mucolytic medications help to break up thick mucus in the lungs, making it easier to clear the airways. Examples of mucolytics include dornase alfa and hypertonic saline.
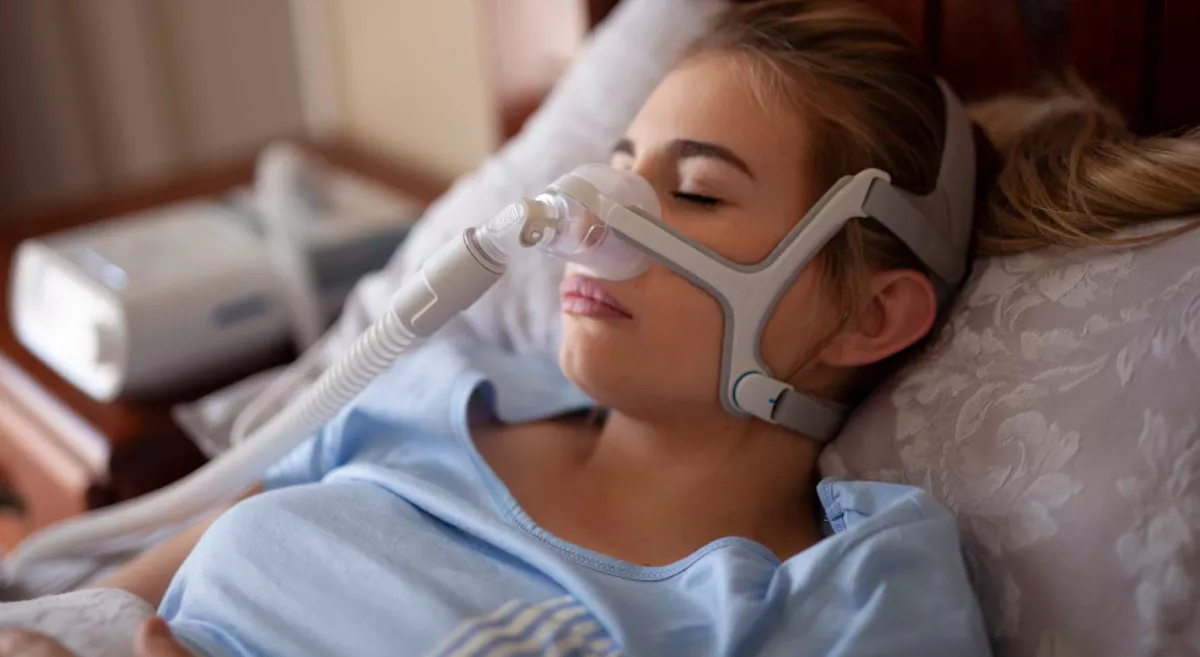
Airway clearance techniques
Airway clearance techniques are exercises that can help to loosen and remove mucus from the lungs. Examples of airway clearance techniques include chest physiotherapy, postural drainage, and the use of oscillating devices.
Vaccinations
Vaccinations against certain types of infections, such as pneumococcal and influenza, can help to prevent respiratory infections that can worsen bronchiectasis.
Management of underlying conditions
If bronchiectasis is caused by an underlying condition, such as cystic fibrosis or immune system disorders, it is important to manage these conditions appropriately to help manage bronchiectasis.
It's important to note that treatment for bronchiectasis should be individualized to each patient, and a thorough evaluation by a pulmonologist or respiratory therapist is recommended to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
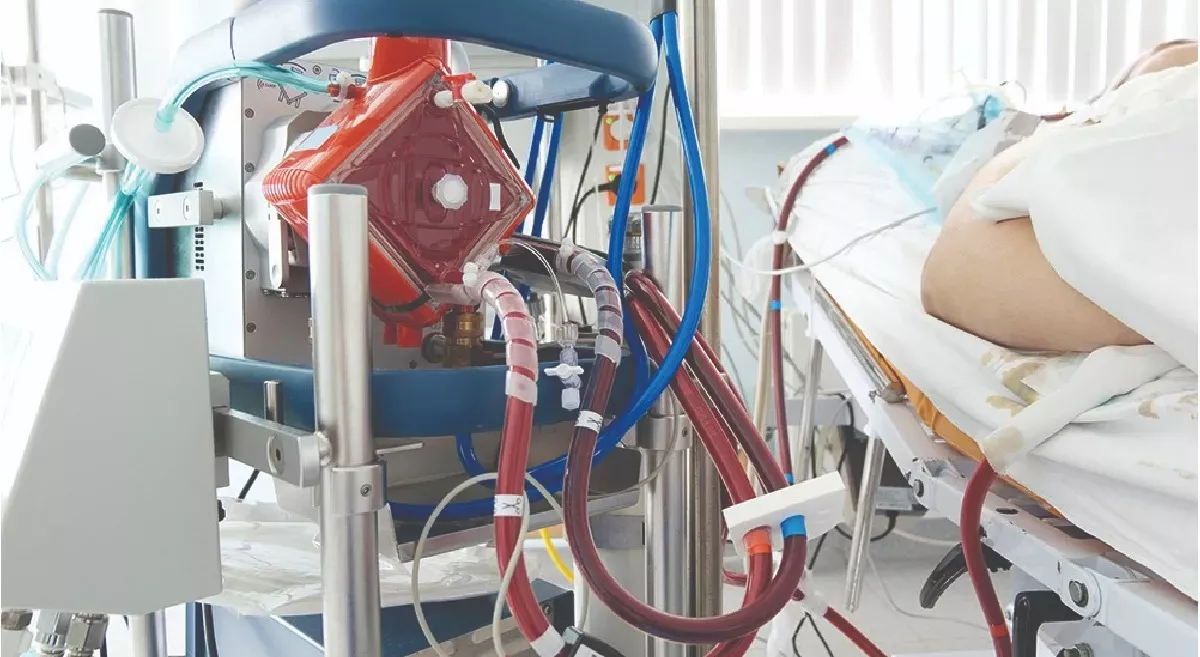
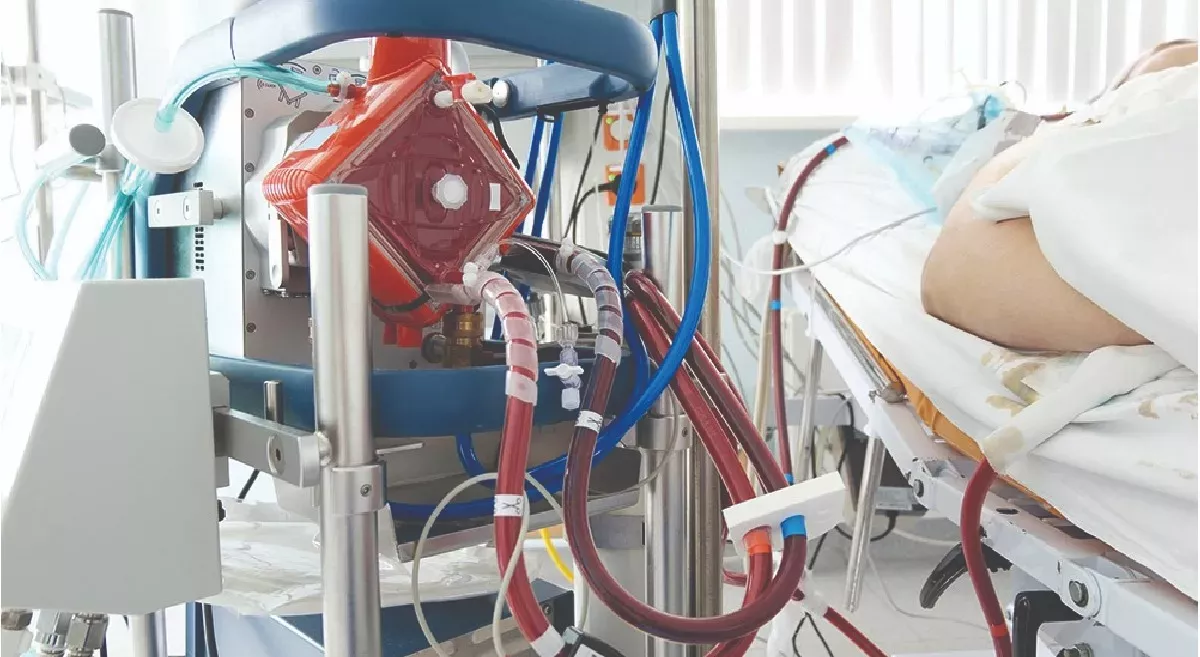
Lung Transplantation
Lung transplantation may be considered for patients with severe bronchiectasis who have not responded to other medical treatments. Lung transplantation is a complex surgical procedure that involves removing the patient's damaged lungs and replacing them with healthy lungs from a donor. The goal of lung transplantation is to improve the patient's quality of life and increase their survival.
However, not all patients with bronchiectasis are candidates for lung transplantation. Patients who are considered for lung transplantation undergo a thorough evaluation to determine their suitability for the procedure. The evaluation process typically includes a review of the patient's medical history, physical examination, lung function tests, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. In addition, the patient may undergo psychological and social evaluations to determine their ability to manage the demands of post-transplant care.
Some factors that may influence the decision to proceed with lung transplantation in patients with bronchiectasis include the severity and progression of the disease, the presence of complications such as respiratory failure or pulmonary hypertension, and the patient's overall health and comorbidities.
After lung transplantation, patients require lifelong immunosuppressive medication to prevent rejection of the transplanted lung. They also require close monitoring for complications, such as infections and organ rejection, and may require ongoing medical management and rehabilitation.
It's important to note that lung transplantation is a complex procedure, and not all patients are good candidates for the procedure. The decision to proceed with lung transplantation should be made in consultation with a multidisciplinary team, including pulmonologists, transplant surgeons, and other specialists.